Figure EV3. Further characterization of RNA‐seq data and the tests of IL6 and Gldc on chemical reprogramming.
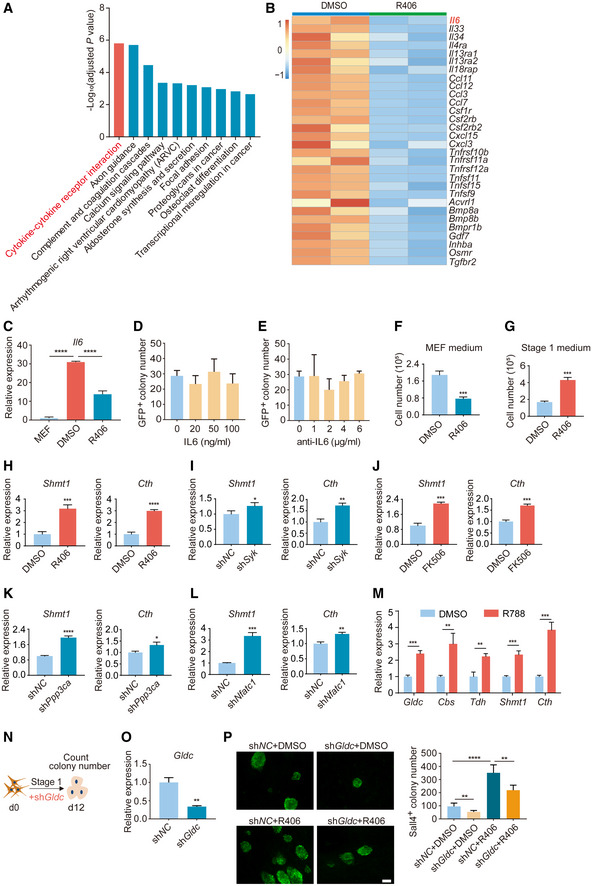
-
AKEGG analysis of downregulated genes in R406‐treated reprogramming intermediates. Statistical significance was assessed by Benjamini–Hochberg method.
-
BHeatmap of RNA‐seq data for the normalized expression (z score) of genes involved in cytokine–cytokine receptor interaction (A).
-
CRT–qPCR analysis of Il6 expression in MEFs and reprogramming intermediates treated with DMSO and R406. n = 3.
-
DGFP+ colony number on d24 of samples treated with IL6 protein. n = 3.
-
EGFP+ colony number on d24 of samples treated with anti‐IL6 antibody. n = 3.
-
FCell number on d4 of samples cultured in MEF medium supplemented with DMSO or R406. n = 3.
-
GCell number on d4 of samples cultured in Stage 1 medium supplemented with DMSO or R406. n = 3.
-
H–LRT–qPCR analysis of Shmt1 and Cth gene expression after treatments of R406, shSyk, FK506, shPpp3ca, and shNfatc1 on d8 of reprogramming. n = 3.
-
MRT–qPCR analysis of Gldc, Cbs, Tdh, Shmt1, and Cth gene expression after R788 treatment on d8 of reprogramming. n = 3.
-
NDiagram showing the procedure of shGldc virus infection at the early stage of reprogramming.
-
ORT–qPCR analysis of Gldc expression in MEFs infected with shNC and shGldc viruses. n = 3.
-
PImmunofluorescence of Sall4 in shNC‐ and shGldc‐infected cells with and without R406 treatment on d12. n = 5. Scale bar, 100 μm.
Data information: All data are presented as mean ± SD. Statistical significance was assessed by the two‐tailed Student’s t‐test, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001.
