Figure 1.
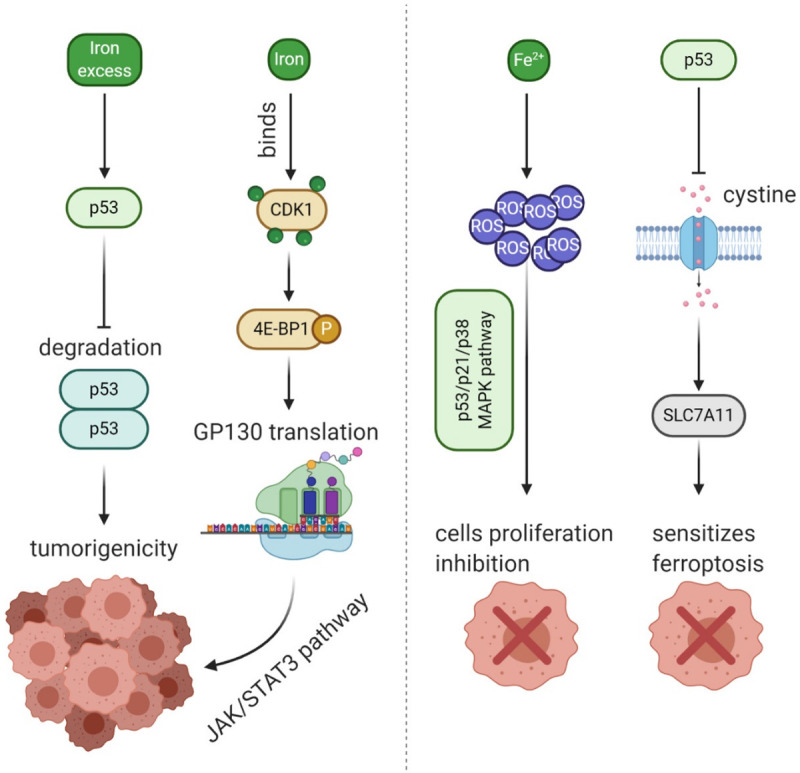
The schematic diagram of some iron-related pathway in cancer cells. The excess iron would impact the degradation of p53, then promote the tumorigenicity; iron binds the protein CDK1 activate 4E-BP1, then lead to translation of GP130 via JAK/STAT3 pathway; Fe2+ produce ROS in cancer cells which inhibits the proliferation of cells trough p53/p21/p38 MAPK pathway; p53 could also inhibit the uptake of cystine to repress expression of SLC7A11, and then promote the ferroptosis in cancer cells.
