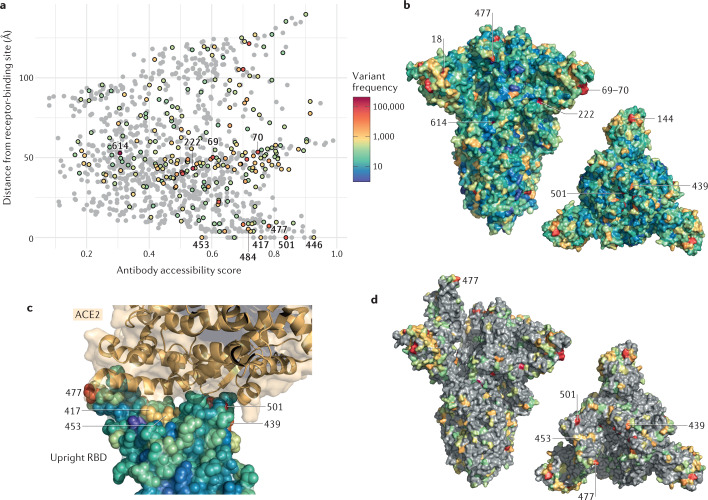
Fig. 3. Structural context of spike amino acid mutations in the global virus population.
Spike amino acid residues are coloured according to the frequency of amino acid substitutions or deletions. Variants (retrieved from CoV-GLUE) are based on 426,623 high-quality sequences downloaded from the Global Initiative on Sharing All Influenza Data (GISAID) database on 3 February 2021. a | Points representing each spike amino acid residue are positioned according to the antibody accessibility score and the distance to the nearest residue in the receptor-binding site. Residues with at least 100 sequences possessing a substitution or deletion are coloured according to the frequency scale shown, with the remainder shaded grey. b | Spike protein in closed form with all residues coloured according to the frequency scale shown; a trimer axis vertical view (left) and an orthogonal top-down view along this axis (right) are shown. c | A close-up view of the receptor-binding domain (RBD) bound to ACE2 (RCSB Protein Data Bank ID 6M0J95), with RBD residues shown as spheres coloured by amino acid variant frequency and ACE2 shown in gold. Amino acid variants are present at high frequency in positions at the RBD–ACE2 interface. d | Spike protein in open form with residues where at least 100 sequences possessing a substitution are highlighted; a trimer axis vertical view (left) and an orthogonal top-down view along this axis (right) are shown.