Fig. 3. ST2 plays a critical role in the hepatoprotective effect of eosinophils.
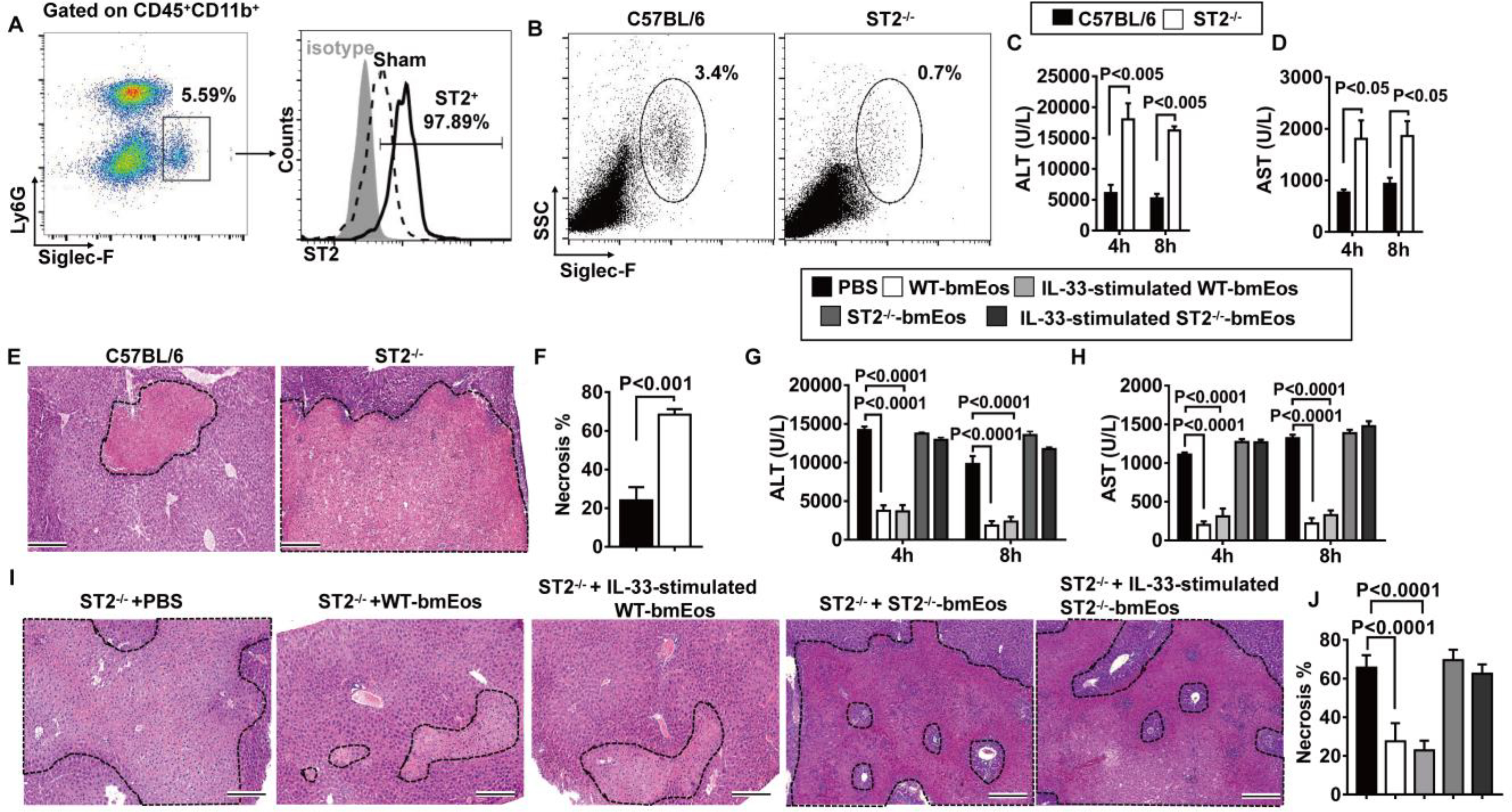
(A) Liver nonparenchymal cells were isolated at 24 hours after reperfusion. ST2 expressions on eosinophils were measured by flow cytometry. Data shown represent samples from four mice. (B to F) WT and ST2−/− mice were subjected to hepatic IR surgery (n = 4 mice per group). Hepatic eosinophil accumulation, shown as proportions among CD45+ nonparenchymal cells, was measured at 4 hours after reperfusion (B). Serum concentrations of ALT (C) and AST (D) were measured at 4 and 8 hours after reperfusion. Liver necrosis (scale bars, 200 μm) was examined at 24 hours after reperfusion (E) and quantified (F). (G to J) ST2−/− mice were adoptively transferred with WT-bmEos, IL-33–stimulated WT-bmEos, ST2−/−-bmEos, IL-33–stimulated ST2−/−-bmEos, or PBS as control at 24 hours before hepatic IR surgery (n = 3 in the ST2−/− + PBS, n = 4 in all remaining groups). Serum concentrations of ALT (G) and AST (H) were measured at 4 and 8 hours after reperfusion. Liver necrosis (scale bars, 200 μm) was examined at 24 hours after reperfusion (I) and quantified (J). A two-tailed unpaired Student’s t test with Welch’s correction was performed in (F). A two-way ANOVA was performed in (C), (D), (G), (H), and (J).
