Fig. 6. -mediated IL-33 signaling stimulates eosinophils to produce IL-13.
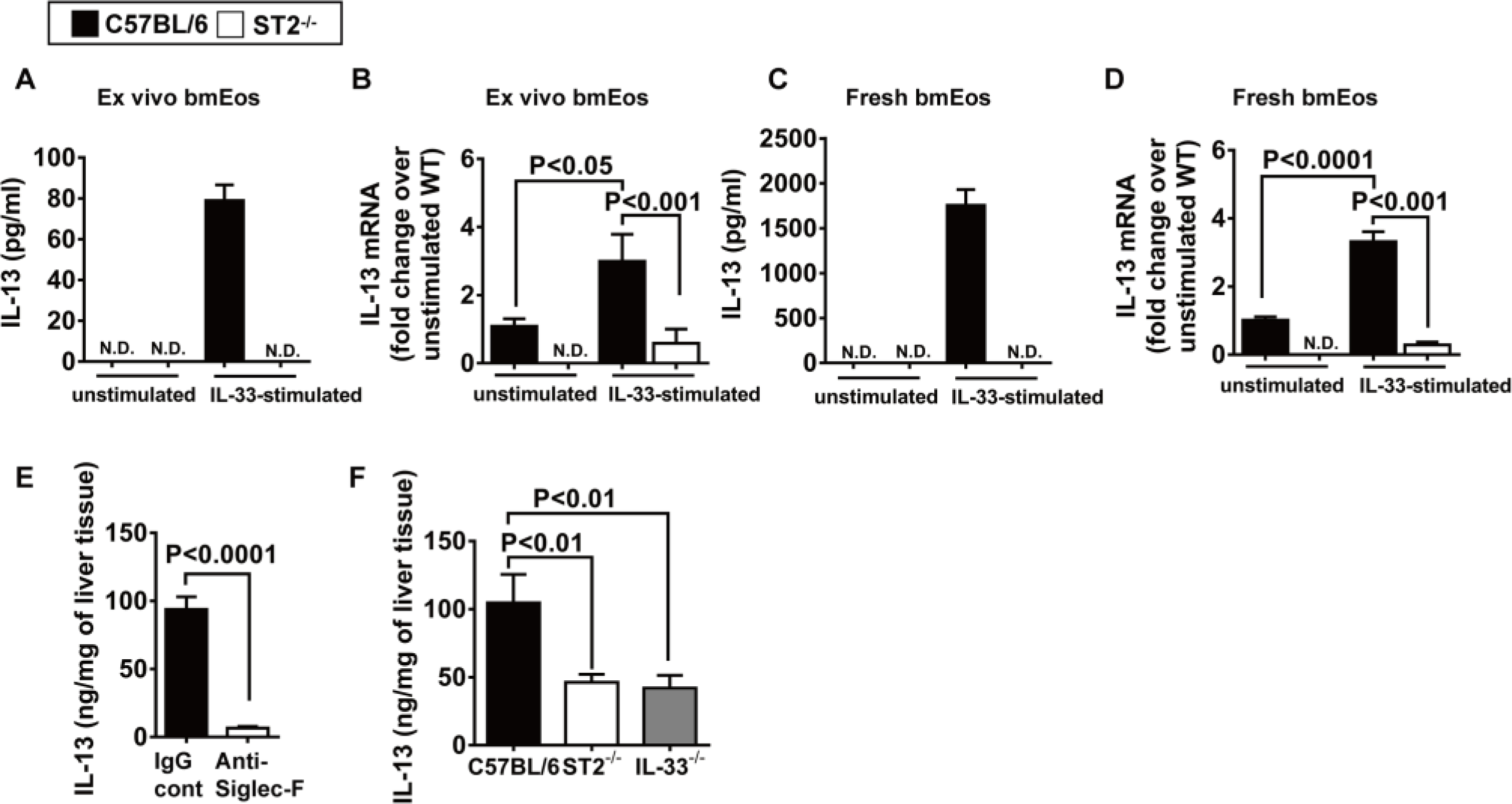
ST2 (A and B) bmEos were generated ex vivo from C57BL/6 and ST2−/− mice (n = 5 mice per group). IL-13 concentrations in culture supernatants (5 × 106 cells per well) (A) and mRNA expression (B) were measured after stimulation with recombinant mouse IL-33 for 24 hours by ELISA and qPCR, respectively. N.D. indicates not detectable. (C and D) Eosinophils (1 × 106 cells per well) were freshly isolated from the bone marrow of C57BL/6 and ST2−/− mice (n = 4 mice per group) and stimulated with IL-33 for 24 hours. IL-13 protein in culture supernatants (C) and mRNA (D) expression were measured by ELISA and qPCR, respectively. (E) WT C57BL/6 mice were treated with anti–Siglec-F antibody to deplete eosinophils or IgG as control at 24 hours before hepatic IR surgery (n = 4 mice per group). IL-13 concentration in the livers was measured at 4 hours after reperfusion by ELISA. (F) C57BL/6, ST2−/−, and IL-33−/− mice were subjected to IR surgery (n = 5 in C57BL/6, n = 7 in ST2−/−, and n = 5 IL-33−/− mice). IL-13 concentrations in the livers were measured at 4 hours after reperfusion by ELISA. A two-tailed unpaired Student’s t test with Welch’s correction was performed in (E). A one-way ANOVA was performed in (F). A two-way ANOVA was performed in (A), (B), (C), and (D).
