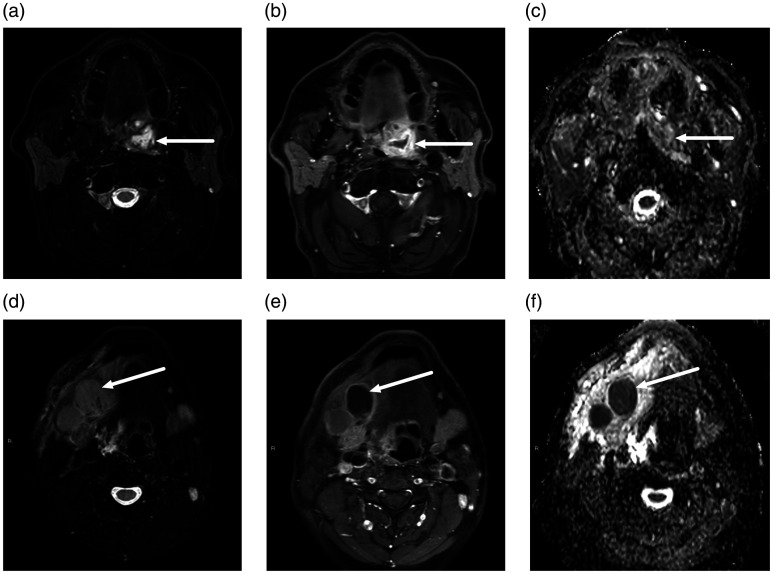
Fig. 5.
FN (a–c) and FP (D–F) abscesses on MRI in two different patients. Axial MRI slices (a, d, T2-weighted Dixon water; b, e, gadolinium-enhanced T1-weighted Dixon water; c, f, ADC from DWI). FN abscess, top row (a–c): a 62-year-old man presented with a sore throat. MRI demonstrated an abnormal collection with enhancing rim and non-enhancing center superior to the left palatine tonsil (arrows). ADC values were high rather than low in the non-enhancing part, and therefore, an abscess was not diagnosed. However, subsequent surgery found an abscess. FP abscess, bottom row (d–f): A 43-year-old man with neck swelling. MRI showed lymphadenitis and tissue edema on the right suprahyoid neck, and one enlarged submandibular space lymph node with no enhancement and low ADC values (arrows). Suppurative lymphadenitis (intranodal abscess) was diagnosed based on these MRI findings. However, surgery demonstrated necrotic lymphadenitis, but no purulence. ADC, apparent diffusion coefficient; DWI, diffusion-weighted imaging; FN, false negative; FP, false positive; MRI, magnetic resonance imaging.