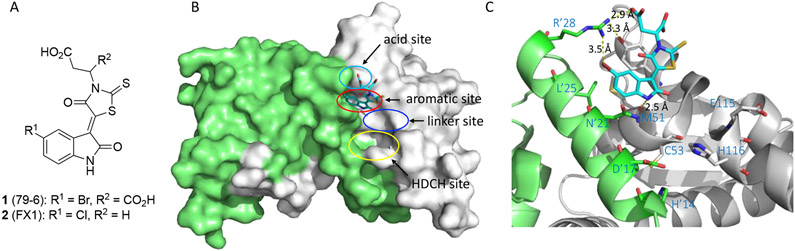
Figure 2.
(A) Chemical structures of early BCL6 inhibitors 1 and 2. (B) Binding mode of compound 1 to BCL6BTB (PDB ID: 3LBZ). Compound 1 was shown in cyan and BCL6BTB monomers are shown in green and gray, respectively. The binding pocket of BCL6BTB LG includes four continuous binding sites: acid site (cyan), aromatic site (red), linker site (blue) and HDCH site (yellow). (C) Detailed binding mode of inhibitor 1 in complex with BCL6BTB. The key residues from BCL6BTB were shown as sticks. The distances of highlighted H-bond interactions were shown in angstrom (Å).