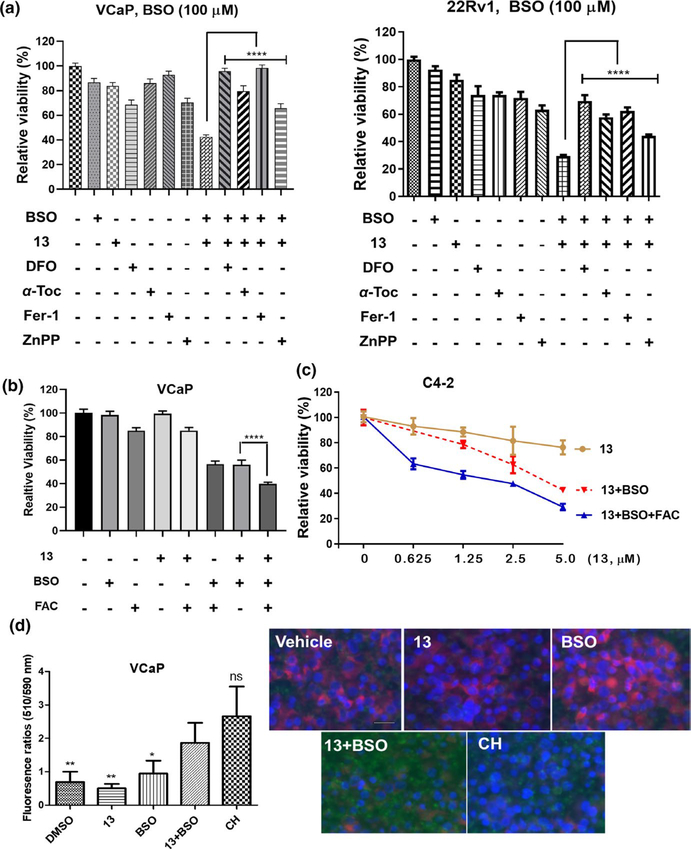
FIGURE 6.
13 and buthionine sulfoximine (BSO) combination induces ferroptosis in PCa cells. (a) 13 plus BSO-caused viability suppression is rescued by antioxidants, iron chelator, and HO-1 inhibitor. VCaP or 22Rv1 cells were treated with 13 (VCaP, 2.5 μM; 22Rv1, 5 μM), DFO (100 μM), α-Tocopherol (α-Toc, 100 μM), ferrostatin-1 (Fer-1, 0.5 μM), or ZnPP (3 μM) individually or in combination for 24 hr. BSO (100 μM) was added 16 hr prior to other agents. Values stand for mean ± SD (n = 6–8). ****p < .0001. (b, c) Exogenous iron enhances the potency of 13 plus BSO. VCaP cells were treated with 13 (1 μM), BSO (100 μM), and FAC (25 μM) individually or in combination for 24 hr. BSO was added 16 hr prior to other agents (b). Values stand for mean ± SD (n = 6–8), ****p < .0001. Similarly, C4–2 cells were treated by 13 (0.6–5 μM) or its combination with BSO (100 μM) and FAC (25 μM). BSO was added 16 hr prior to other agents (c). Data were plotted as mean ± SD (n = 6–8). Viability was assessed using MTT assay. FAC, ferric ammonium citrate. (d) Combination of 13 and BSO increased lipid peroxidation in VCaP cells. Cells were incubated with CH (100 μM, positive control) for 2 hr, BSO (100 μM) or 13 (2.5 μM) for 24 hr. Combinatorial treatments were conducted by pretreating cells with BSO for 16 hr, followed by 13 for 24 hr. Lipid peroxidation was characterized as the ratio (left) of fluorescence emission at 510 nm and 590 nm using BODIPY-C11 fluorescent reporter. Data were plotted as mean ± SD (n = 5), *p < .05, **p < .01 versus 13 and BSO combination. Fluorescence images of the treated cells were shown on the right. Cell nuclei were stained with Hoechst 33342 in blue. Scale bar, 25 μm