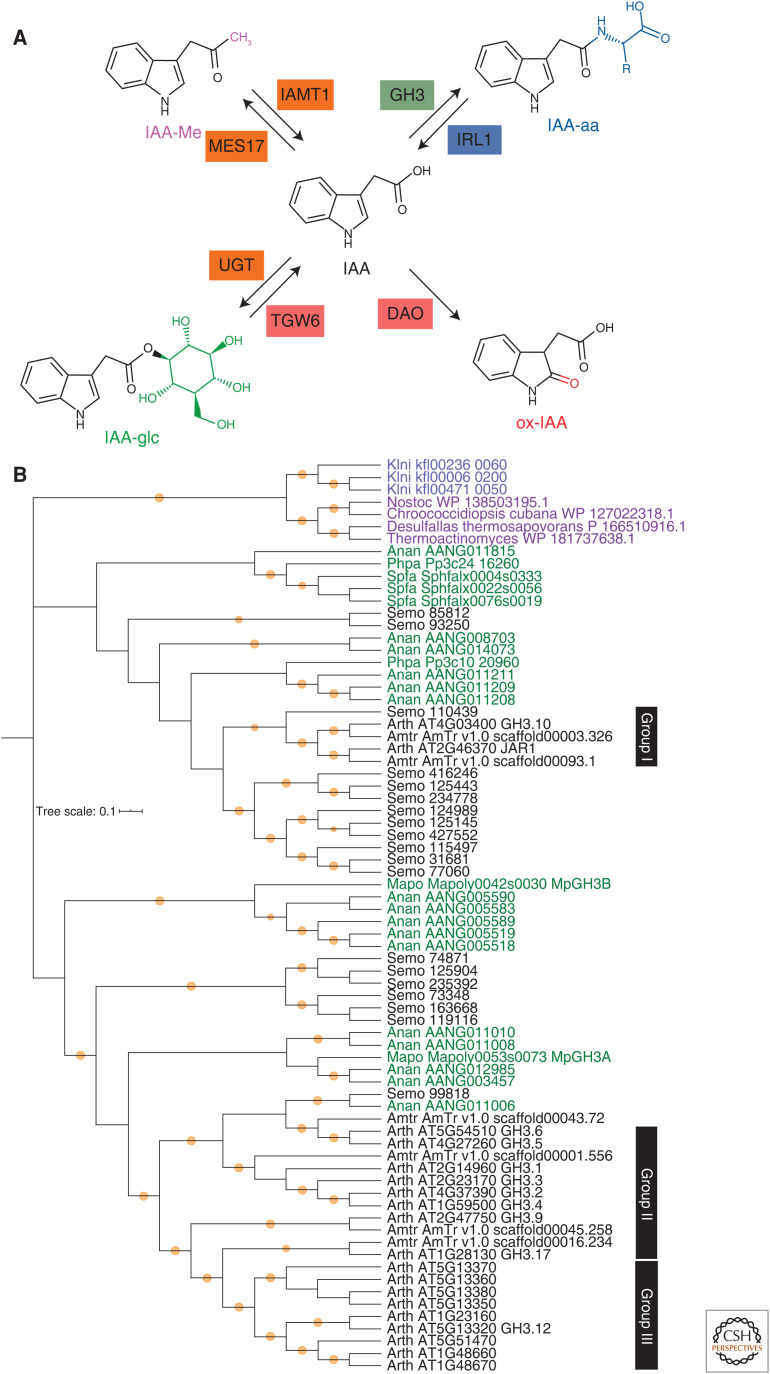
Figure 3.
Indole-3-acetic acid (IAA) is modified into several inactive forms in land plants. (A) IAA is inactivated by conjugation with amino acids (IAA-aa: blue) or sugars (IAA-glc: green), oxidation (oxIAA: red), and methylation (IAA-Me: magenta), and reactivated by enzymes indicated. The enzyme box color indicates conservation among charophycean algae + land plants (blue), land plants (green), seed plants (orange), or angiosperms (red). (B) Phylogenetic reconstruction of the GH3 protein family. The tree highlights two factors to consider when tracing the evolutionary history of genes. First, similar sequences may not be orthologous, but rather derived ultimately from independent sources (e.g., the Klebsormidium and land plant GH3 genes). Second, classifications based on analyses of sequences from only derived taxa (e.g., GH3 classes based on angiosperm sequences may fail to recognize phylogenetic diversity found outside the derived taxa). Protein sequences were collected from GenBank, Phytozome, and the Klebsormidium nitens genome website using blastp search with threshold E-value = 1.0 × 10−20, and aligned using the MUSCLE program (Edgar 2004) implemented in MEGA X (Kumar et al. 2018). Alignment positions with more than 50% gaps were removed using the Phyutility program (version 2.2.6; code.google.com/p/phyutility/downloads/list) and then sequences with more than 30% gap in the alignment were removed. The phylogenetic tree was constructed in MEGA X using an LG + G model with bootstrap replicates = 500. Orange circles indicate bootstrap values more than 0.75. Black: Tracheophytes (Arabidopsis thaliana [Arth], Amborella trichopoda [Amtr], Selaginella moerrendorffii [Semo]), green: bryophytes (Anthoceros angustus [Anan], Marchantia polymorpha [Mapo], Physcomitrium patens [Phpa], Sphagnum fallax [Spfa]), blue: K. nitens (Klni), purple: bacteria. Groups I to III are based on data in Staswick et al. (2005).