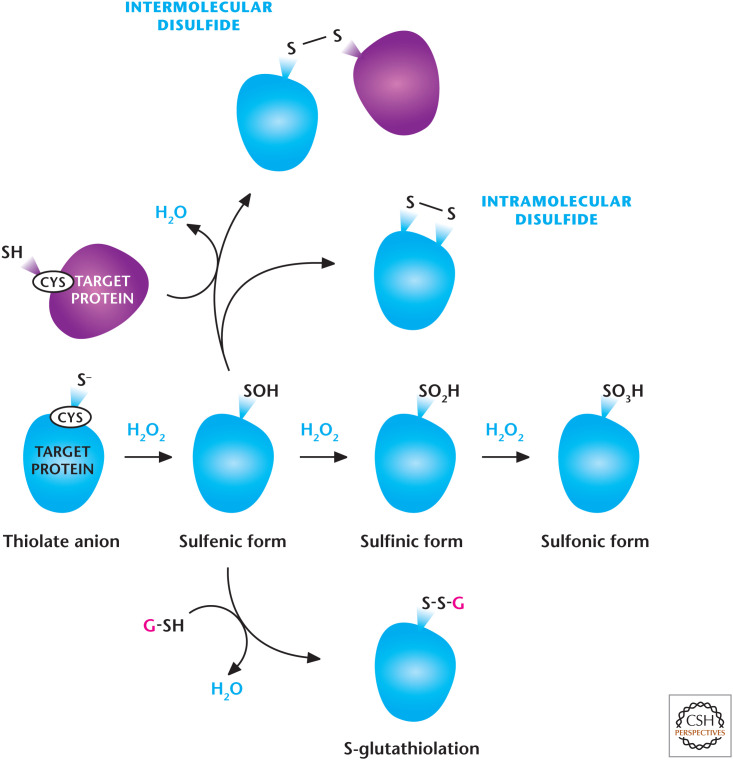
Figure 8.
H2O2-dependent signaling. H2O2 regulates signaling pathways by oxidation of thiol groups on cysteines within proteins that show a low pKa, allowing the cysteine thiol group to exist as a thiolate anion (S−). H2O2 readily oxidizes thiolate, yielding SO−. Under high concentrations of H2O2, SO− can undergo further oxidation to generate SO2− and SO3−. SO− can undergo further modifications including intra- or intermolecular disulfide bonds and S-gluthathiolation. (Modified from Finkel 2011.)