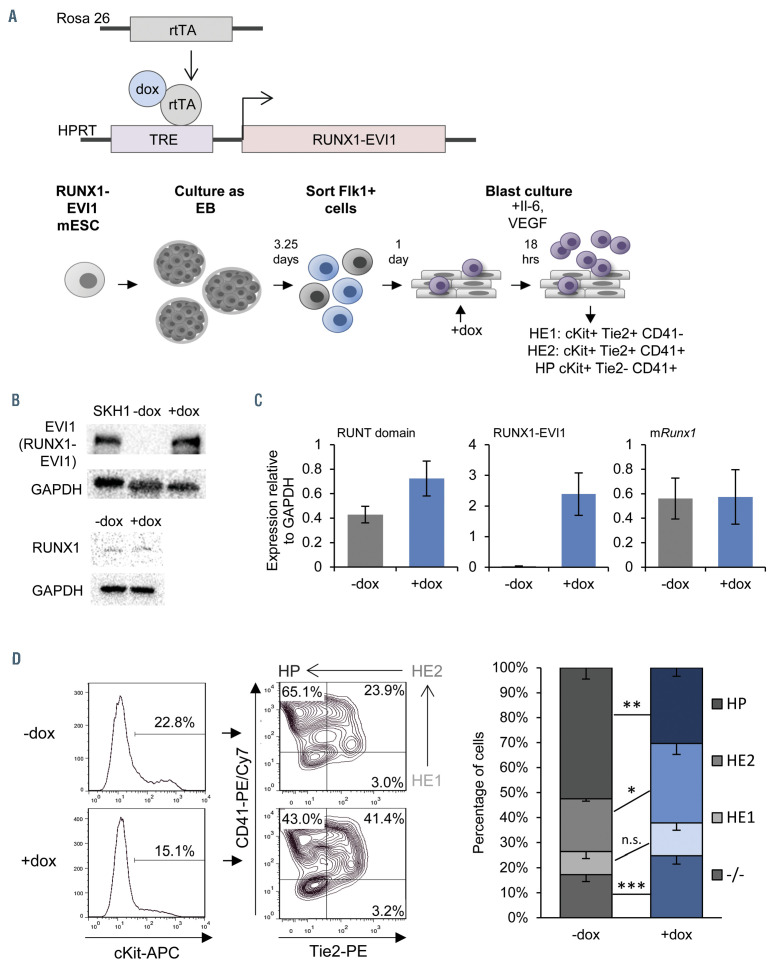
Figure 1.
Induction of RUNX1-EVI1 perturbs Runx1 dependent endothelial to hematopoietic transition. (A) Overview of the generation of dox-inducible RUNX1-EVI1 embryonic stem cells (ESC), in vitro differentiation of ESC to hematopoietic progenitors and timing induction of RUNX1-EVI1. (B) RUNX1-EVI1 was expressed at a comparable level to that in the human t(3;21) cell line SKH-1 shown by western blot. Note that the antibody against EVI-1 does not recognize the endogenous mouse protein. RUNX1 protein levels were unaffected by induction of RUNX1-EVI1. (C) Expression of RUNX1-EVI1 was at a physiological level, equal to that of the endogenous Runx1, shown by quantitative reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction, normalized to glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase (Gapdh). Runt domain primers bind the 5’ end of the gene and so both endogenous Runx1 and RUNX1-EVI1 are detected, mRunx1 primers bind the 3’ end and so only endogenous Runx1 is detected. (D) The composition of the day 2 blast culture, 18 hours following doxycycline (dox) induction, was analyzed by flow cytometry using antibodies against cKit, Tie2 and CD41; representative plots for -dox and +dox samples are shown (left, with the Tie2/CD41 plots pre-gated by cKit+) with the average percentage of each population (right), error bars represent standard error of the mean, n=5, *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.005.