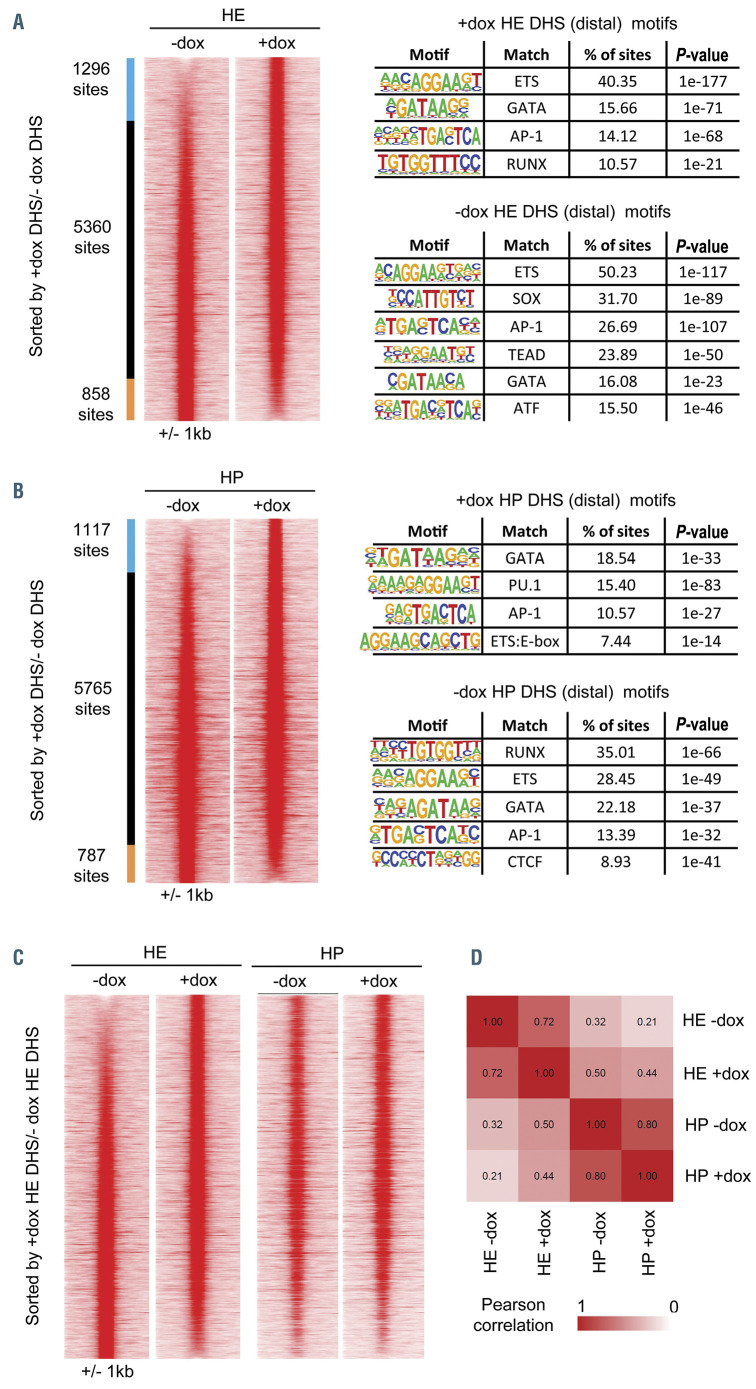
Figure 4.
RUNX1-EVI1 induction causes specific changes to chromatin accessibility. Comparison of distal DNase I hypersensitive sites sequencing (DNaseI-seq) peaks in (A) hemogenic endothelium (HE) cells (cKit+, Tie2+, CD41-/+) and (B) hematopoietic progenitor (HP) cells (cKit+, Tie2-, CD41+). Peaks are ordered according to the fold-difference of the normalized tag-count between -dox and plus doxycycline (+dox) treated cells and are presented as a heatmap of the tag-density for each sample. Peaks that are specific to a sample (fold-difference >2) are indicated as colored bars to the left of the density plots, with the number of peaks in each group shown. The results of a de-novo motif search conducted within the specific sets of peaks are also shown (C) Comparison of the tag-density profiles of the peaks found in HE cells to the same sites measured in HP cells (D) Heatmap showing the results of hierarchical clustering of the pearson correlation values of the distal DNaseI hypersensitive sites (DHS). The actual pearson correlation values are shown on the heatmap.