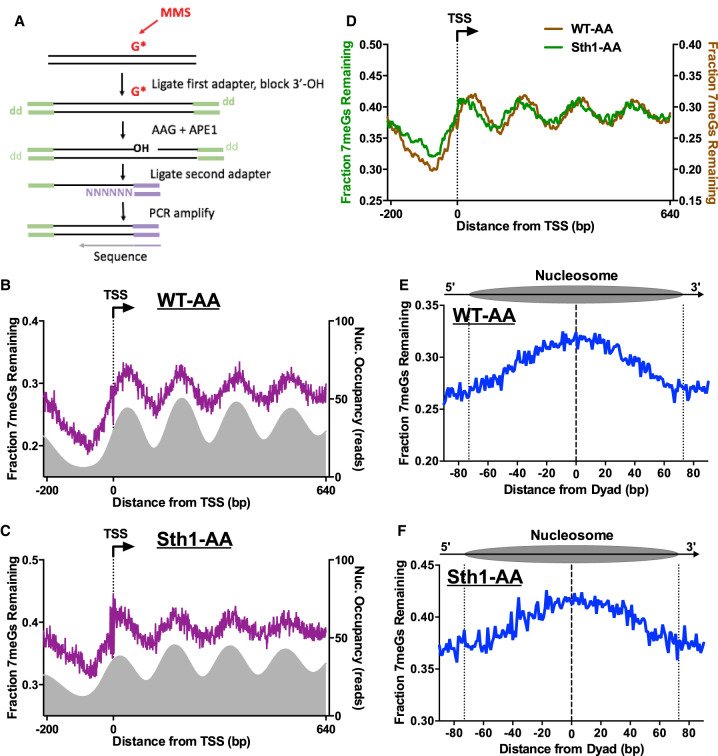
Figure 6.
RSC regulates BER in chromatin. (A) Schematic of the NMP-seq method. Yeast was exposed to 0.4% MMS to induce alkylation damage (primarily 7-methylguanine [7meG], represented by G*), and the resulting N-methylpurine (NMP) lesions are mapped using the indicated method. Adapted from Mao et al. (2017). (B,C) NMP-seq analysis of unrepaired 7meG lesions remaining after 2 h of repair of WT-AA (B) and Sth1-AA cells treated with rapamycin (C). Because 7meG lesions are not thought to be repaired by TC-NER, both DNA strands are combined and plotted in aggregate. Data are shown for positions −200 bp upstream of and +640 bp downstream from the TSS. Nucleosome positions for WT-AA are from vehicle-treated Sth1-AA cells, whereas those for Sth1-AA are from rapamycin-treated Sth1-AA cells (Kubik et al. 2018). (D) Overlay of unrepaired 7meG lesions following 2-h repair in WT-AA and Sth1-AA cells treated with rapamycin to highlight that the shift in mapped lesions corresponds to the shift in nucleosomes toward the TSS that occurs in RSC-depleted cells. NMP-seq data are smoothed in GraphPad Prism using a second-order polynomial and 7 bp on each side. (E,F) NMP-seq analysis of 7meG repair on both DNA strands of nucleosomes in WT-AA and Sth1-AA cells. Nucleosome positions for WT-AA are from vehicle-treated Sth1-AA cells, whereas those for Sth1-AA are from rapamycin-treated Sth1-AA cells (Kubik et al. 2018). Dotted lines at positions −73 and +73 bp from the dyad center indicate the boundary of the nucleosome core particle.