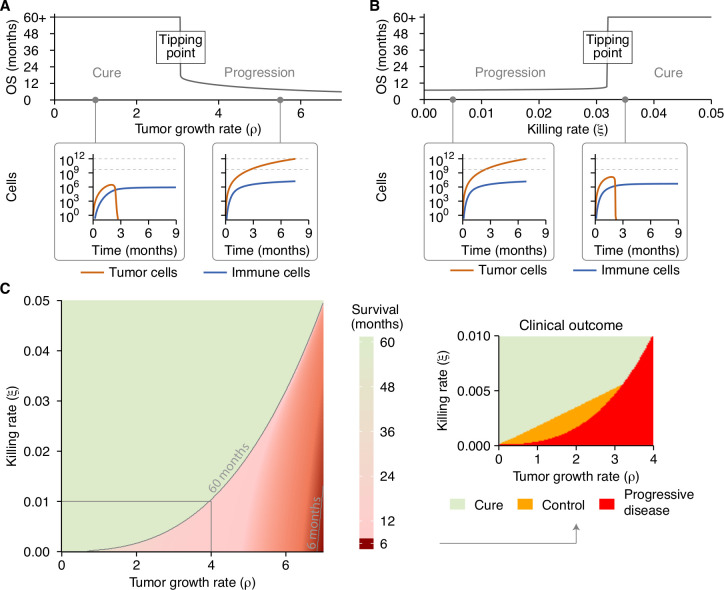
Figure 2.
A tipping point in the tumor-immune interaction determines a patient’s outcome. (A) A gradual increase in tumor growth reveals a tipping point, where long-term survival (immune control; inset 1) abruptly changes to short-term survival (immune evasion; inset 2). (B) A similar analysis reveals a tipping point along the immune axis, again differentiating short-term survival (immune evasion; inset 1) from long-term control (immune control; inset 2). (C) The tipping point is present across the entire range of parameters examined. Cure and progressive disease are the dominant states, whereas subclinical tumor control only occurs within a limited parameter range (inset). Simulation parameters are shown in online supplemental table 2. OS, overall survival.