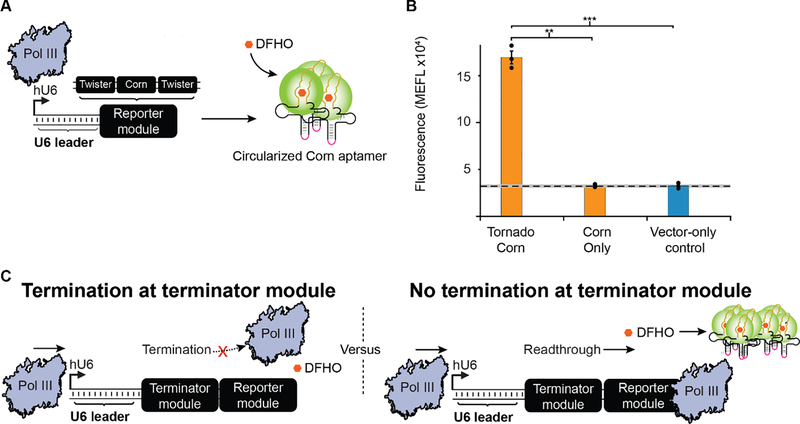
Figure 1: Development of an assay for measuring Pol III termination in human cells.
A) Schematic overview of the construct design of the Tornado system. A human U6 promoter drives Pol III transcription of a ‘Reporter module’, comprising a Corn aptamer (yellow line) which is embedded within a tRNA scaffold and flanked by two twister self-cleaving ribozymes. The ribozymes’ self-cleavage results in a 5’ hydroxyl and a 3’ end consisting of a 2’,3’-cyclic phosphate which is recognized and ligated (pink line) by the endogenous protein RtcB, increasing its stability. Ribozyme self-cleavage and ligation leaves a circularized Corn aptamer that is stabilized by the tRNA scaffold. When DFHO is bound to the Corn aptamer, this dye becomes fluorescent. B) The addition of Tornado to the Reporter module enables quantification of Pol III transcription in cellulo. Colored bars represent the average of 3 biological replicates (circles). The dashed line indicates the average signal from the vector-only (negative) control cells, while the grey horizontal bar represents the standard error of the mean (S.E.M) of the signal from these cells; this convention is applied in subsequent figures. Statistical significance was measured using a one-tailed heteroscedastic Welch’s t-test (***p < 0.001). Error bars represent the S.E.M. C) Termination modules were introduced in this study to investigate the effect of different RNA sequences and structures on Pol III termination. Shown here are expected assay outcomes as a function of termination (left) or readthrough (right) at the Terminator module.