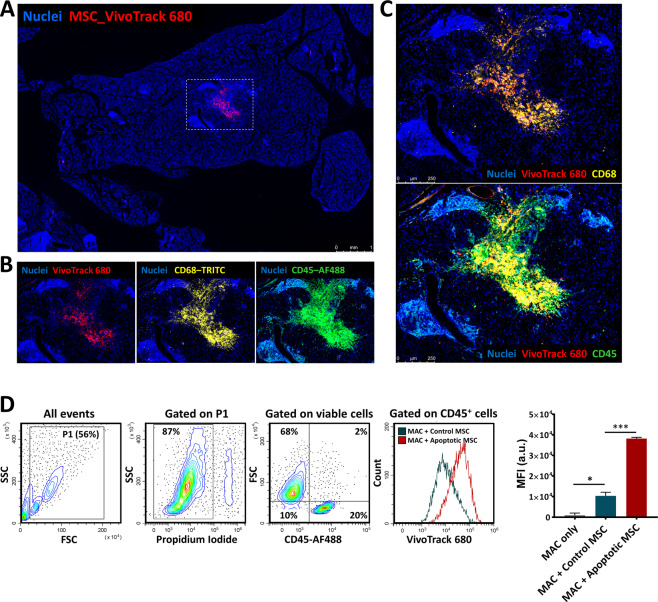
Fig. 5. Infiltration of inflammatory cells after intrapancreatic transplantation of MSC.
A Low-magnification scan of the pancreas at 7 days after transplantation of Luc+ VT680+ MSC; box indicates the area with a high VT680 signal; B Immunofluorescence images of the region indicated in (A). CD68 immunostaining denotes macrophages infiltrated at the transplantation site; CD45 immunostaining demarcates hematopoietic cells; C High-resolution microscopy of the region indicated in (A) showing the presence of cells with co-localized signal of VT680 and CD68 molecule (upper image) and co-localized signal of VT680 and CD45 molecule (lower image), thus suggesting the presence of macrophages that engulfed VT680+ MSC or VT680+ MSC-derived apoptotic bodies. D Flow cytometry analysis of peritoneal macrophages isolated from syngeneic mice co-cultured with healthy (control) or apoptotic MSC. Apoptotic MSC were obtained after 48-h culture with pro-inflammatory cytokines. Note the increased phagocytic activity of macrophages when in presence of apoptotic cells as compared to healthy cells.