Figure 1.
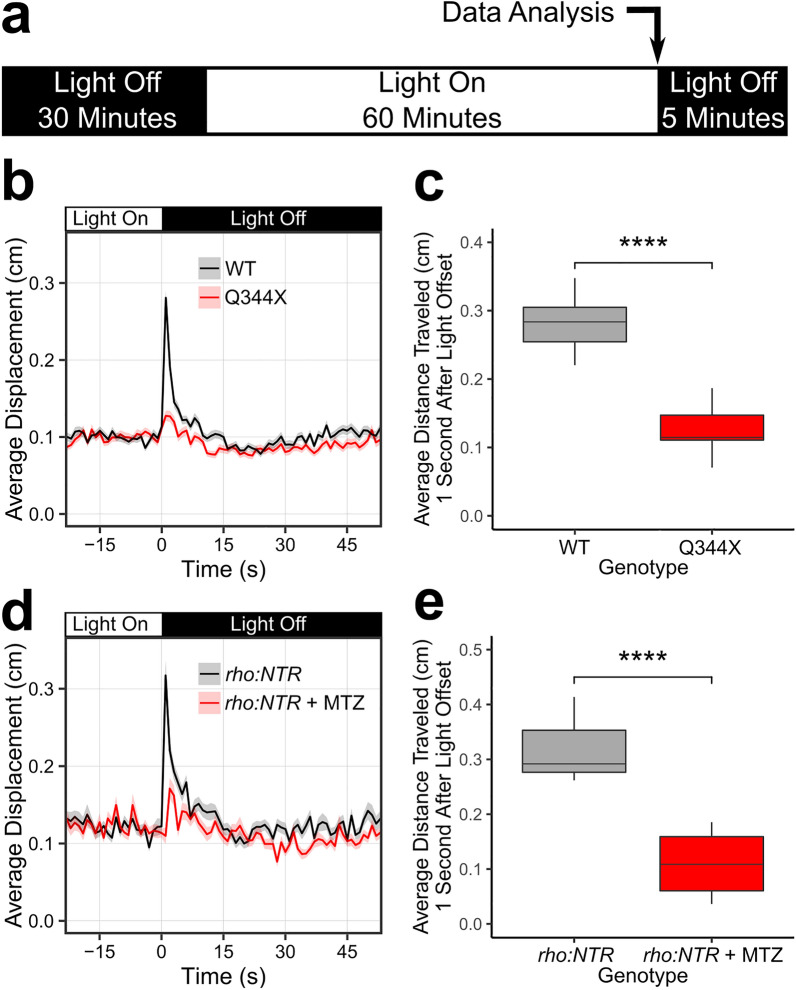
The Q344X larvae displayed a diminished scotopic light-off VMR driven by rods. (a) Schematic of the VMR protocol. On 7 dpf, larvae were habituated to the machine in darkness for 30 min. Then, the light stimulation was turned on and the plate was illuminated for 60 min. After that, the light was turned off. In this study, we mainly analyzed the VMR at light offset (light-off VMR) as indicated by the arrow. (b) The light-off VMR of wildtype (WT, black trace) and Q344X (red trace) larvae at 0.01 lx. The light was turned off at Time = 0. Each trace shows the average larval displacement of 18 biological replicates with 48 larvae per condition per replicate. The corresponding color ribbon indicates ± 1 standard error of the mean (s.e.m.). (c) Boxplot of the average larval displacement of WT and Q344X larvae one second after light offset. The average displacement of WT larvae (µ ± s.e.m.): 0.281 ± 0.036 cm, N = 18) was significantly larger than that of Q344X larvae (0.127 ± 0.031 cm, N = 18) (Welch’s Two Sample t-test, T = 13.2, df = 33.2, p value < 0.0001). To confirm this scotopic VMR was driven by rods, we chemically-ablated rods in larvae and subjected them to the same scotopic VMR assay (d, e). (d) The light-off VMR of larvae with nitroreductase-expressing rods treated with metronidazole (rho:NTR + MTZ, red trace) and without metronidazole (rho:NTR, black trace). Each trace shows the average displacement of 6 biological replicates with 24 larvae per condition per replicate. The corresponding color ribbon indicates ± 1 s.e.m. (e) Boxplot of the average displacement of rho:NTR and rho:NTR + MTZ larvae one second after light offset. The average displacement of untreated rho:NTR larvae (µ ± s.e.m.): 0.317 ± 0.061 cm, N = 6) was significantly larger than that of rho:NTR + MTZ larvae (0.110 ± 0.062 cm, N = 6) (Welch’s Two Sample t-test, T = 5.9, df = 10, p value < 0.0001).