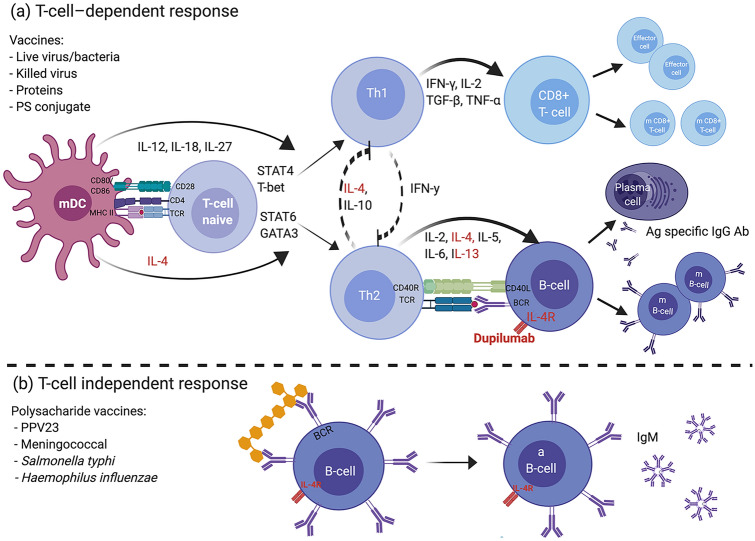
Fig. 1.
Vaccine response and the potential impact of dupilumab. Dupilumab is a human (IgG4) monoclonal antibody anti-IL-4 receptor that blocks the α-subunit shared by IL‐4R receptor type I and II, decreasing the signal induced by IL-4 and IL-13. a T cell-dependent response vaccines generate humoral and cellular responses with immune memory. After recognition of the antigen, APCs (B cells, macrophages, or DCs) present the processed antigen to naive T cells via peptide-MHC II. Co-stimulation between B7 ligands (CD80/CD86) and CD28 on the T cell is required. The type of pathogen determines the cytokine environment, which dictates the development of a specific T cell phenotype. IL-12, secreted by the DC in response to virus infection or intracellular bacteria, promotes polarization towards the TH1 pathway, which secretes IFNγ and activates CD8 + CTLs and phagocytic cells and inhibits TH2 development. In contrast, IL-4 initiates polarization to TH2 pathways and inhibits TH1 development. Via activation of STAT6 and GATA3, IL-4 promotes gene expression of IL‐4, IL‐5, and IL‐13. APCs trigger a TH2 cell response in the presence of thymic stromal lymphopoietin, IL-25, and IL-33 produced by epithelial cells. TH2 responses drive B cell activation, requiring co‐stimulatory signals through the CD40–CD40L (CD154) from the TH cell and leading to differentiation into a plasma cell, isotype class switching, antibody secretion and clonal expansion of memory B cells. IL-4 acts as a B cell growth factor, and IL-6 assists in maturation of the antibody response. Theoretically, blocking IL-4 does not impair response to viral infection. b Polysaccharide vaccines elicit a T cell–independent response. The antigen directly interacts with B cells, producing antibodies limited to IgM without immunologic memory. Live bacteria: BCG. Live virus: influenza (intranasal), measles, mumps, oral polio, rotavirus, rubella, varicella zoster, yellow fever. Killed virus: inactivated poliovirus. PS conjugated: Haemophilus influenzae type B, meningococcal and pneumococcal conjugated. Protein: acellular pertussis, diphtheria, hepatitis B, human papillomavirus, influenza, tetanus. Ab antibody, aB cell activated B cell, Ag antigen, APC antigen presentation cell, BCG bacille Calmette-Guerin, BCR B cell receptor, CTL cytotoxic T lymphocytes, DC dendritic cell, IFN interferon, Ig immunoglobulin, IL interleukin, m B cell memory B cell, m CD8 + T cell memory T cell, mDC mature dendritic cell, MHC major histocompatibility complex, PS polysaccharide, TH T helper, TNF tumor necrosis factor, TCR T cell receptor, TGF transforming growth factor. Created with BioRender.com