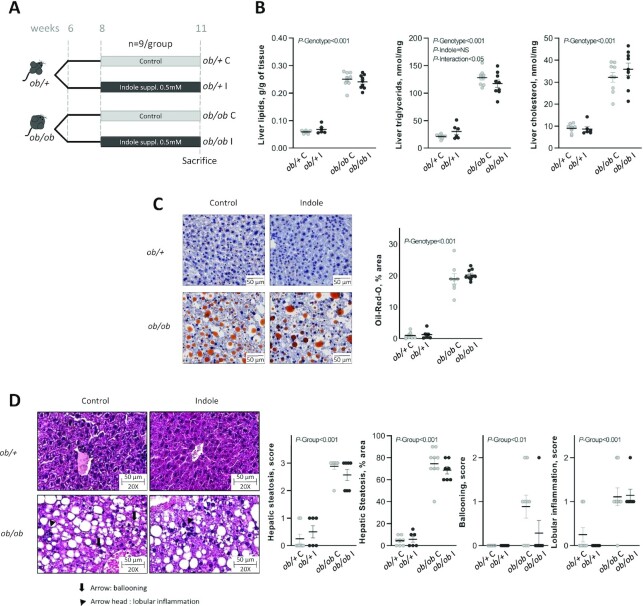
FIGURE 1.
Effect of indole supplementation (0.5 mM) in ob/+ and ob/ob mice for 3 wk (A: experiment 1) on (B) hepatic lipids and (C, D) hepatic histology. (C) Representative Oil Red O (ORO)-stained liver sections for each experimental group (bar = 50 μm) and mean ORO relative area per group. Two-factor ANOVA was used with genotype and indole treatment as fixed effects and the cage as random effect. (D) Representative H&E-stained liver sections for each experimental group, ballooning being signaled by an arrow and lobular inflammation by an arrow head. Scoring was performed on 3 criteria: steatosis (0–3 and % area), ballooning (0–2), and lobular inflammation (0–2). Scoring was analyzed using a nonparametric Kruskal–Wallis test with the experimental group as factor. Data are presented as means ± SEM, n ≥6/group. H&E, hematoxylin and eosin; NS, not significant (P ≥ 0.05); ob/+ C, control ob/+ mice; ob/+ I, indole-treated ob/+ mice; ob/ob C, control ob/ob mice; ob/ob I, indole-treated ob/ob mice; suppl., supplemented.