Fig. 1. Differences between human pluripotent stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes (hPSC-CMs) and ventricular cardiomyocytes from adult cardiac tissue.
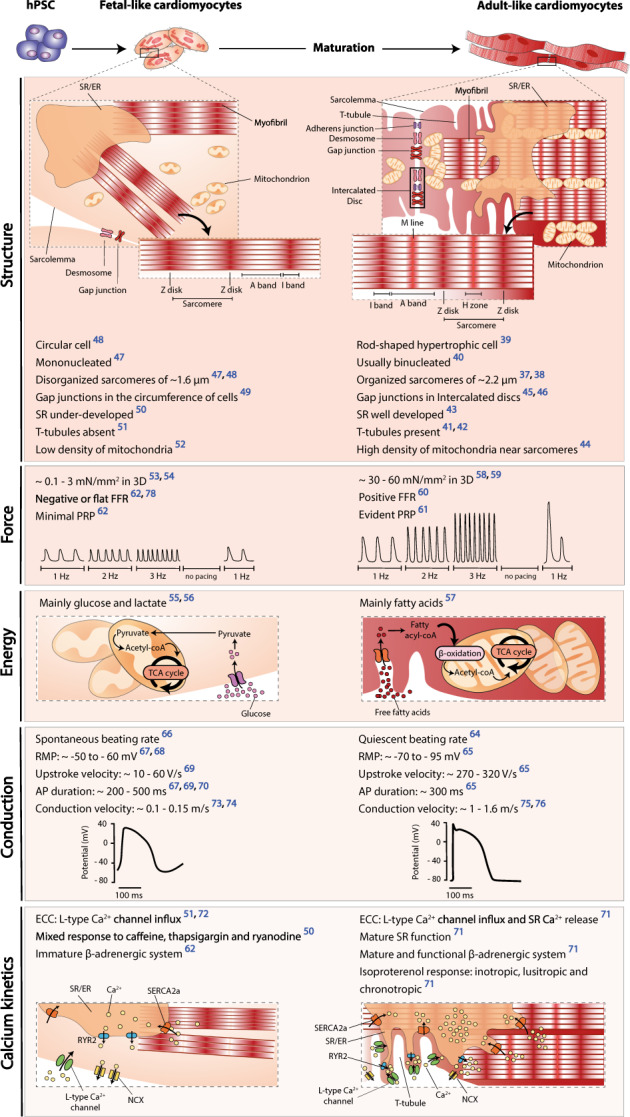
hPSC-CMs obtained from the differentiation of pluripotent stem cells present fetal-like features in respect to structural and ultrastructural organization, contractile force, metabolism, and electrophysiological function. AP action potential, ECC excitation–contraction coupling, FFR force–frequency relationship, hPSCs human pluripotent stem cells, NCX sodium–calcium exchanger, PRP post-rest potentiation, RMP resting membrane potential, RYR2 ryanodine receptor type 2, SERCA2a sarcoplasmic/endoplasmic reticulum calcium-ATPase 2a, SR/ER sarcoplasmic/endoplasmic reticulum.
