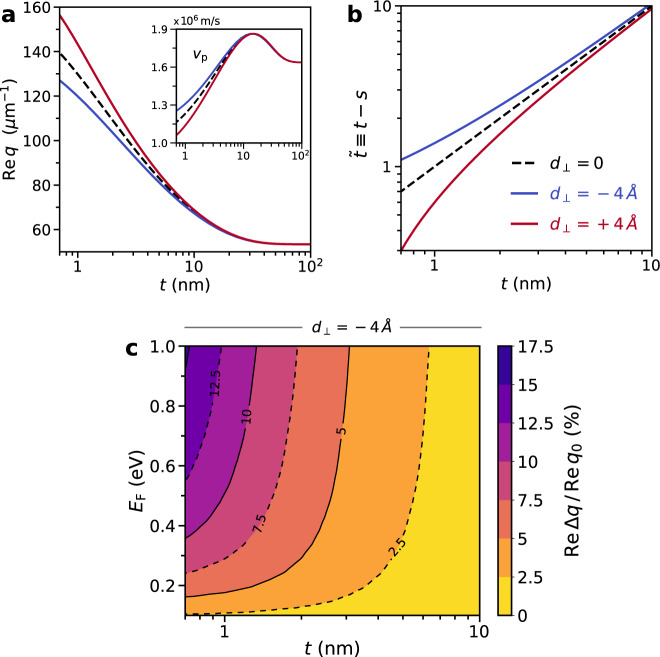
Fig. 4. Nonclassical corrections probed by AGPs.
a AGP’s wavevector as a function of the graphene–metal separation t, contrasting the metal’s response based on classical (d⊥ = 0) and quantum (d⊥ = ±4 Å) treatments. Inset: corresponding group velocity . b Dependence of the renormalized graphene–metal separation versus t. Setup parameters: rs = 3, γm = 0.1 eV, ϵd = 4, EF = 0.3 eV, and γ = 8 meV; we assume an excitation at λ0 = 11.28 μm (ω0 ≈ 110 meV or f0 ≈ 26.6 THz)32. c Relative quantum shift of the AGP wavevector, , with Δq ≡ q0 − q where q0 and q denote the AGP wavevector associated with d⊥ = 0 and d⊥ = −4 Å, respectively. The results presented in both a and c are based on the exact, numerical solution of Eq. (1).