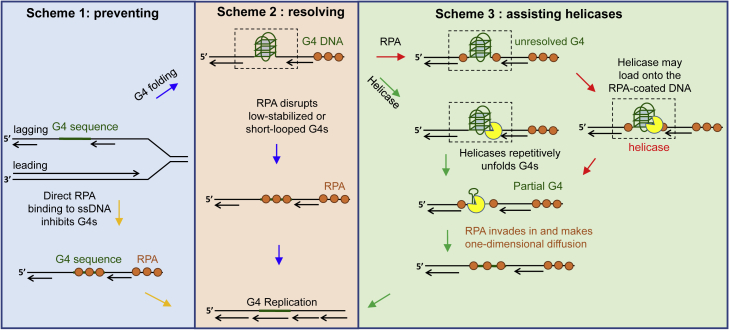
Figure 8.
The proposed mechanisms of RPA in eliminating G4 structures
DNA replication was taken for example. G4 structures can be formed in both the leading and lagging strands. Here the G4 in the lagging strand was shown. In scheme 1, RPA quickly and directly binds to the exposed G4 sequence, directly inhibiting its folding. Once the G4 sequence escapes RPA, it may well fold into G4 structures. In scheme 2, RPA is able to constantly disrupt the low stabilized G4s or repetitively unfold the short-looped G4s. However, RPA is poor at resolving G4s with long loops and high stability. Then in scheme 3, RPA assists the specialized helicases to remove those G4 obstacles no matter RPA coats the adjacent ssDNA at first or the helicase binds to the G4 substrate at first.