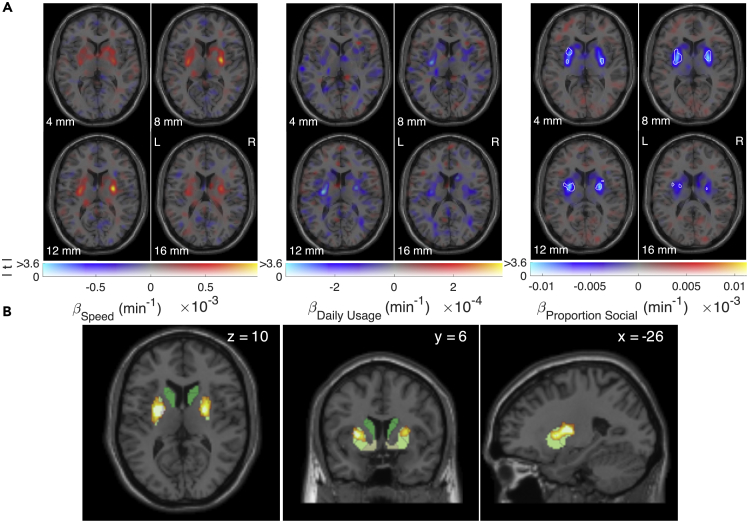
Figure 1.
Whole-brain regression of dopamine synthesis capacity on speed, daily usage, and proportion of social interactions
(A) Whole-brain individual difference regression weights of dopamine synthesis capacity predicted by smartphone interaction speed, interactions per day, and proportion of social interactions. White boundaries encompass voxels at (uncorrected) p < 0.001, indicating that bilateral putamen synthesis capacity reflects proportion of social interactions; display format from (Zandbelt, 2017).
(B) Proportion social interaction clusters (PFWE < 0.05, small volume correction) resulting from permutation-based, threshold-free cluster enhancement (Smith and Nichols, 2009). Clusters overlap an independently defined segmentation of the striatum including the dorsal and medial caudate nucleus (dark green), anterior and posterior putamen (yellow-green), and ventral striatum (pale yellow). Note that similar clusters were obtained following thresholded (p < 0.001) cluster formation (see Figure S2).