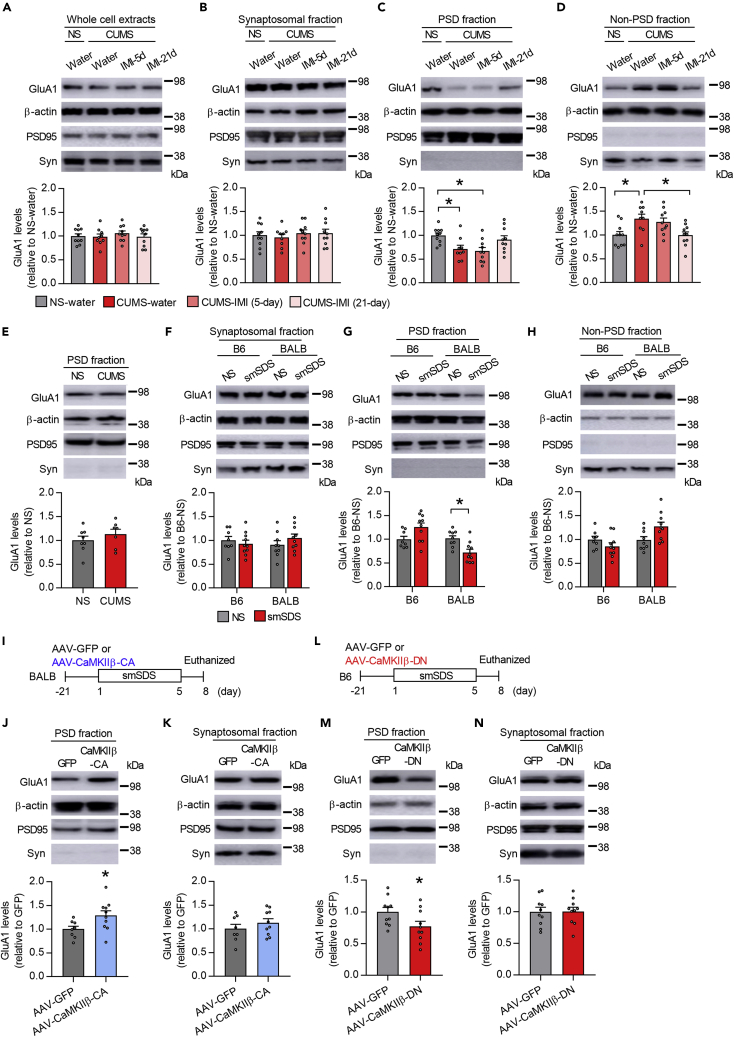
Figure 4.
Disruption of GluA1 expression in PSD fraction in susceptible mice is mediated by CaMKIIβ dysfunction
(A–D) Immunoblot estimation of GluA1 level in the whole cell extract (A), synaptosomal fraction (B), postsynaptic membrane (PSD) fraction (C), and non-PSD fraction (D) of the vCA1 in BALB mice exposed to chronic ultra-mild stress (CUMS) or non-stress (NS), treated with imipramine (IMI) or water. PSD95 and synaptophysin (Syn) were used as PSD and non-PSD markers, respectively. n = 9–10 mice per group.
(E) Immunoblot estimation of GluA1 levels in the PSD fraction of the vCA1 in B6 mice exposed to CUMS. n = 7–8 mice per group.
(F–H) Immunoblot estimation of GluA1 levels in the synaptosomal fraction (F), PSD fraction (G), and non-PSD fraction (H) of the vCA1 in BALB and B6 mice exposed to subchronic and mild social defeat stress (smSDS) or NS. n = 8–10 mice per group.
(I) Experimental timeline. BALB mice were injected with AAV-CaMKIIβ-CA or AAV-GFP into the vCA1, subjected to smSDS, and euthanized to measure GluA1 levels.
(J and K) Immunoblot estimation of GluA1 levels in the PSD fraction (J) and synaptosomal fraction (K). n = 8–10 mice per group.
L. Experimental paradigm. B6 mice were injected with AAV-CaMKIIβ-DN or AAV-GFP into the vCA1, subjected to smSDS, and euthanized to measure GluA1 levels.
(M and N) Immunoblot estimation of GluA1 levels in the PSD (M) and synaptosomal (N) fractions. n = 10 mice per group.
One-way ANOVA followed by a Tukey's post hoc test (in A-D), two-way ANOVA followed by a Tukey's post hoc test (in F-H), and two-tailed Student's t-test (in E, J, K, M, and N) were used for statistical analyses. ∗p < 0.05. Bar graphs show mean ± SEM.
See also Figure S4. Complete statistical summaries are provided in Table S2.