Figure 5.
GluA1 function is crucial for behavioral responses to chronic stress
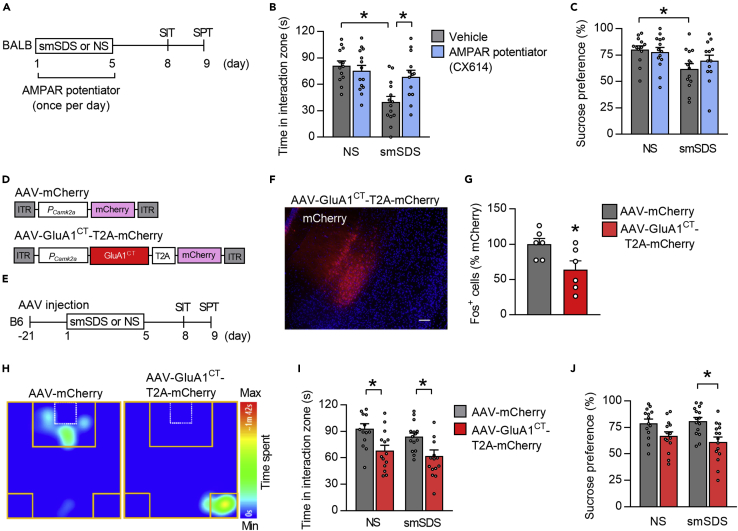
(A) Experimental paradigm. BALB mice were subjected to 5-day subchronic and mild social defeat stress (smSDS). An AMPA receptor potentiator was infused into their vCA1 1 hr before smSDS exposure (day 1 to day 5, once per day). SIT, social interaction test; SPT, sucrose preference test.
(B and C) Treatment with AMPAR potentiator rescues smSDS-elicited reduction of the time in the interaction zone in the SIT (B) and prevents smSDS-induced anhedonia in the SPT (C). n = 13–14 mice per group.
(D) AAV vectors engineered to overexpress a GluA1CT (AAV-GluA1CT-T2A-mCherry) or a control construct (AAV-mCherry). PCamk2a, Camk2a promoter.
(E) Experimental paradigm. B6 mice were injected with AAV-GluA1CT-T2A-mCherry or AAV-mCherry and subjected to 5-day exposure to smSDS.
(F) AAV microinjection into the vCA1. Region-specific expression of mCherry in the vCA1 is shown. Scale bar, 100 μm.
(G) Overexpression of GluA1CT decreases Fos levels in the vCA1 of B6 mice following smSDS exposure. n = 6 mice per group.
(H) Representative examples of behavior traces of stressed mice given either AAV-mCherry or AAV-GluA1CT-T2A-mCherry during the SIT (target session).
(I and J) GluA1CT overexpression reduces time in the interaction zone in the SIT (I) and induces anhedonia in the SPT (J) after smSDS. n = 14–15 mice per group.
two-way ANOVA followed by a Tukey's post hoc test (in B, C, I, and J) and two-tailed Student's t-test (in G) were used for statistical analyses. ∗p < 0.05. Bar graphs show mean ± SEM. See also Figure S5. Complete statistical summaries are provided in Table S2.