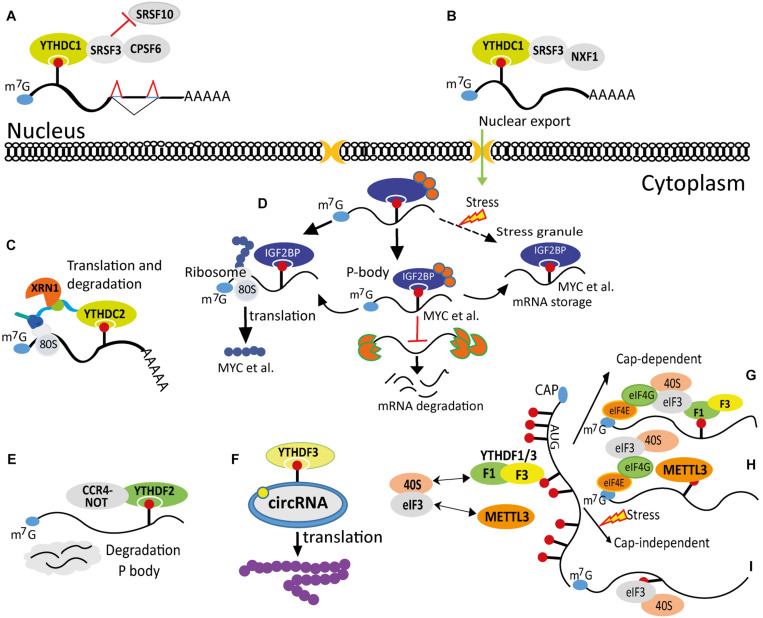
FIGURE 2.
Effects of N6-methyladenosine (m6A) methylation on messenger RNA (mRNA) fate. (A) m6A modification regulates mRNA splicing and polyadenylation via YTHDC1 and its associating factors SRSF3, SRSF10, and CPSF6. (B) m6A modulates mRNA nuclear export through YTHDC1, SRSF3, and NXF1. (C) m6A regulates mRNA translation and stability via YTHDC2-mediated recruitment of the ribosome and the XRN1 exoribonuclease. (D) m6A marks are bound by IGFBPs, which can regulate a subset of mRNA translation, decay in P-body, and storage in stress granules. (E) m6A modification regulates mRNA degradation in P-body through associating with the YTHDF2-CCR4-NOT complex. (F) m6A marks on circRNA modulate its translation via recruiting YTHDF3. (G) m6A marks recruit YTHDF1/YTHDF3 to enhance translation in a Cap-dependent manner. (H) METTL3 serves as an m6A reader and increases translation via recruiting translation initiation complex independent of its methyltransferase activity. (I) m6A directly binds to eIF3 and increases translation in a Cap-independent manner.