Figure 2.
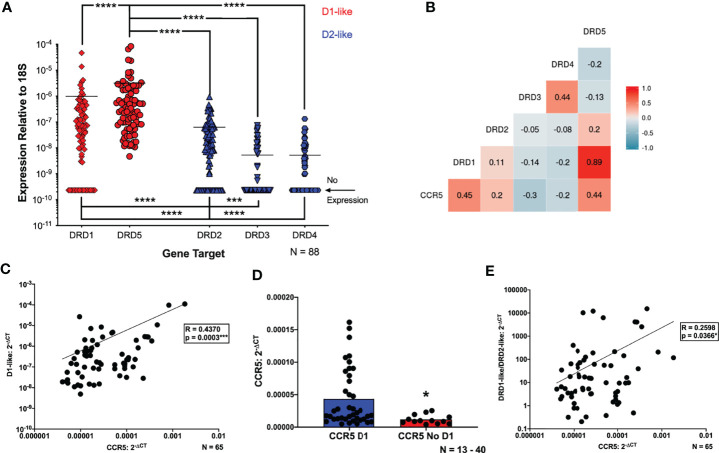
Expression of CCR5 correlates with dopamine receptor expression in hMDM. (A) Quantitative RT-PCR detected mRNA for all subtypes of dopamine receptors (D1R, D2R, D3R, D4R and D5R) in primary human monocyte-derived macrophages (hMDM) (N=88). Expression of all receptors was normalized to 18s for each donor. The D1-like receptors (red dots) were expressed at significantly higher levels than the D2-like receptors (blue dots) (Friedman test, n=88, Friedman statistic 233, ****p < 0.0001; Post-hoc with Dunn’s multiple comparisons, DRD5 vs. DRD1, DRD2, DRD3, or DRD4 ****p < 0.0001, DRD1 vs. DRD3 or DRD4, ****p < 0.0001, DRD2 vs. DRD3, ***p = 0.0003, and DRD2 vs. DRD4, ****p < 0.0001). Correlational analyses were then performed to look at correlations between each dopamine receptor and CCR5 mRNA expression (N=65). A matrix to visualize these correlations is shown in (B), and we found that increased expression of CCR5 is associated with greater expression of the D1-like receptors (CCR5 vs D1, n = 65, Spearman r = 0.4454, ***p = 0.0002, CCR5 vs D5, n = 65, Spearman r = 0.4448, ***p = 0.0002). Increased expression of CCR5 is also associated with decreased DRD3 expression (CCR5 vs D3, n = 65, Spearman r = -0.3007, *p = 0.0149), and no association was found between the other D2-like receptors and CCR5. A number of donors lacked expression of one or more dopamine receptors, so the data were reanalyzed for correlations between CCR5 and the (C) D1-like (DRD1 and DRD5) dopamine receptors. These analyses showed a positive correlation between CCR5 and D1-like receptors (CCR5 vs D1-like dopamine receptors, n = 65, Spearman r = 0.4370, ***p = 0.0003). The connection between D1-like receptors and CCR5 was strengthened by analysis of CCR5 levels in hMDM that did or did not express DRD1. These analyses showed hMDM without DRD1 had significantly lower levels of CCR5 mRNA than those expressing DRD1 (Mann-Whitney test, n = 17 - 48, *p = 0.0218, sum of (D1, No D1) ranks 1737, 408, U=255) (D). This was not done for DRD5 because all donors expressed this receptor. CCR5 levels were also correlated with a D1-like receptor/D2-like receptor ratio (D1/D2 ratio) (E), and we showed a significant, positive correlation between the D1/D2 ratio and CCR5 expression (CCR5 vs D1/D2-like dopamine receptors, n = 65, Spearman r = 0.2598, *p = 0.0366).