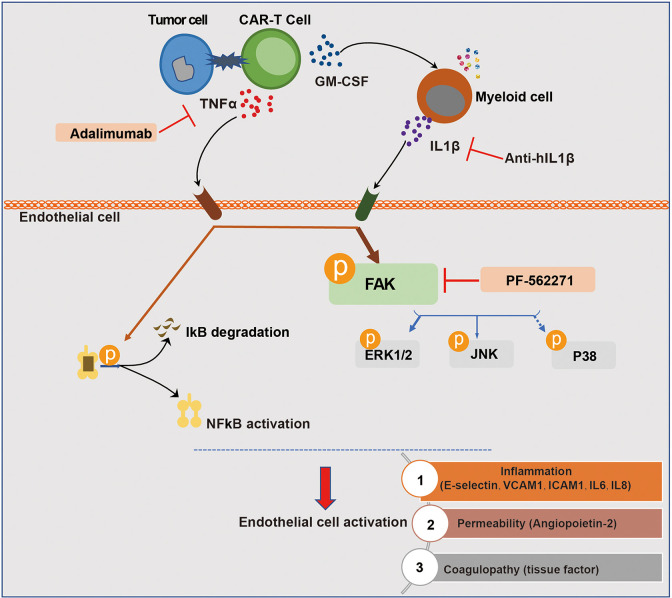
Figure 8.
Schematic description of the role of endothelial activation in CAR-T therapy-induced CRS and neurotoxicity. The recognition of tumor cells by CAR-T cells leads to the activation of CAR-T cells and the production of cytokines. Among the most abundant cytokines secreted by engaged CAR-T cells, TNFα played a major role in inducing endothelial activation. CAR-T cells and tumor cells induced the activation of myeloid cells, leading to the secretion of IL1β which was another important pro-inflammatory cytokine that induces endothelial activation. In this process, FAK, NF-кB, and MAPK were activated. The blockade of TNFα and IL1β with adalimumab and anti-IL1β as well as the inhibition of FAK activity effectively ameliorated endothelial dysfunction induced by CAR-T/tumor cells/myeloid cells in CAR-T therapy.