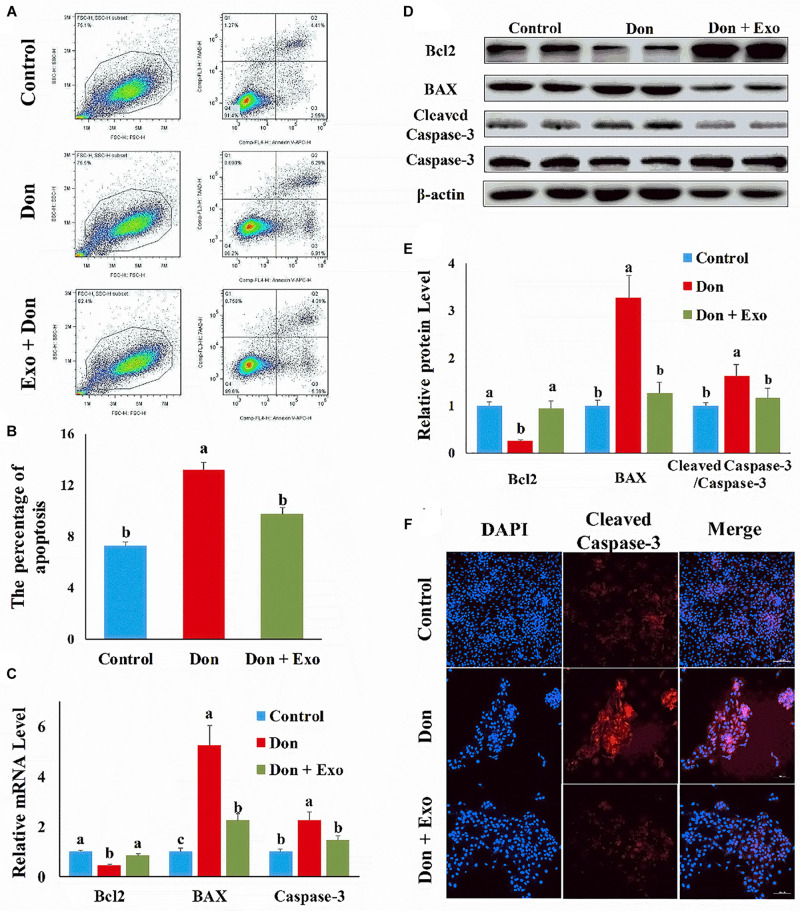
FIGURE 1.
Exosome attenuated deoxynivalenol (Don)-induced intestinal epithelial cell apoptosis. (A) Representative images of apoptosis assay for intestinal epithelial cells by using the apoptosis detection kit. Cells localized in Q4 displayed Annexin V-APC-negative/7AAD-negative viable cells. The cells gated in Q2 and Q3 quadrant displayed Annexin V-APC-positive apoptotic cells. (B) The quantitative result of (A). (C) qPCR results indicated that exosome attenuated Don-induced intestinal epithelial cell apoptosis. (D) Western blot results showed exosome-attenuated Don-induced intestinal epithelial cell apoptosis. (E) The relative protein levels obtained by Western blot (WB) band gray scanning. (F) Representative images of the caspase-3 immunofluorescent staining for apoptotic intestinal epithelial cells. Cleaved caspase-3: red, a molecular marker of apoptosis; DAPI: blue, cell nucleus; Merge: the apoptotic cells. The results were presented as mean ± SEM of triplicate independent experiments for each group. Bars with different letters indicate they are significantly different (p < 0.05). In (F), magnification = × 100; the scale bar on the photomicrographs represents 100 μm. Don, IPEC-J2 cells were exposed to 1.6 μg/ml Don for 12 h. Don + Exo, IPEC-J2 cells were incubated with 2 mg/ml exosome for 24 h, then exposed to 1.6 μg/ml Don for 12 h.