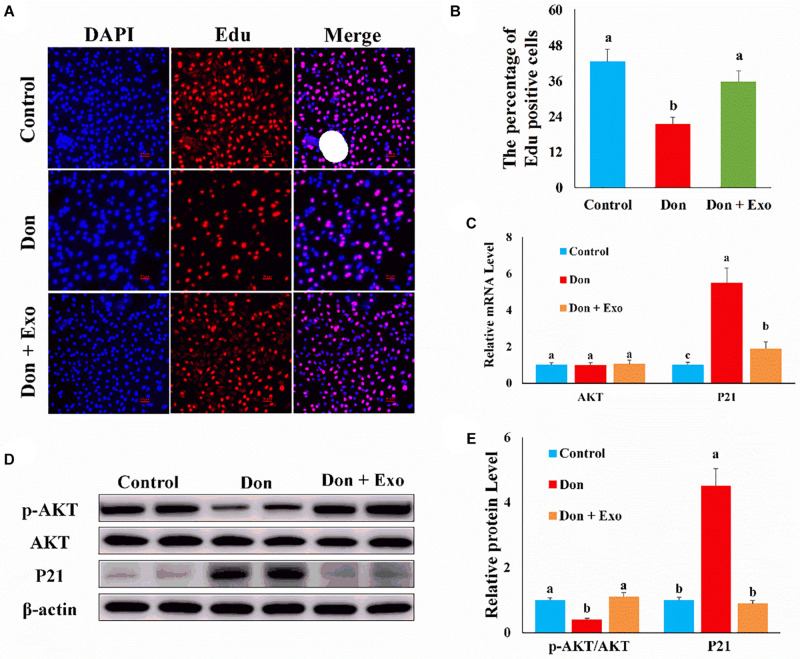
FIGURE 2.
Exosome reversed the inhibitory effect of Don on intestinal epithelial cell proliferation. (A) Representative images of the EdU staining for proliferating intestinal epithelial cells are shown. The cell nucleus was stained with 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI, blue). Proliferating intestinal epithelial cells were labeled with 5-ethynyl-2′-deoxyuridine (EdU) fluorescent dye (red). (B) The quantitative result of (A). (C) qPCR results indicated that exosome reversed the inhibitory effect of Don on intestinal epithelial cell proliferation. (D) Western blot results showed exosome reversed the inhibitory effect of Don on intestinal epithelial cell proliferation. (E) The relative protein levels obtained by WB band gray scanning. Our results were presented as mean ± SEM of triplicate independent experiments for each group. Bars with different letters indicate they are significantly different (p < 0.05). In (A), magnification = × 100; the scale bar on the photomicrographs represents 100 μm. Don, IPEC-J2 cells were exposed to 1.6 μg/ml Don for 12 h. Don + Exo, IPEC-J2 cells were incubated with 2 mg/ml exosome for 24 h, then exposed to 1.6 μg/ml Don for 12 h.