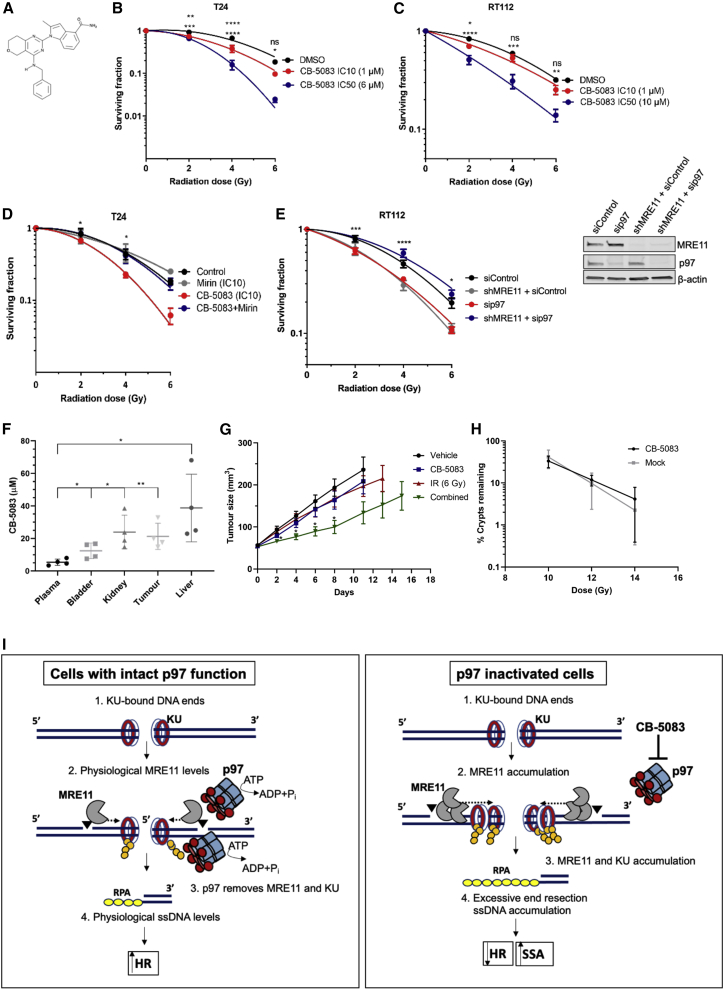
Figure 7.
CB-5083 radiosensitizing effects and acute normal tissue toxicity
(A) Chemical structure of CB-5083.
(B and C) Linear quadratic survival curves of T24 (B) and RT112 (C) cells treated with IR either in combination with CB-5083 IC10 (T24, 1 μM; RT112, 1 μM) and IC50 (T24, 6 μM; RT112, 10 μM), or alone. Statistical significance is indicated on the respective graphs, where the upper row represents IC10 in comparison to the control, and the second row represents IC50 in comparison to the control. NS, not significant; ∗p < 0.05; ∗∗p < 0.01; ∗∗∗p < 0.001; ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001 (two-way ANOVA). See also Figure S2.
(D) Survival of T24 cells after IR and treatment with CB-5083, mirin, or both; n = 2 individual biological experiments in triplicate. Error bars represent ± SEM; two-way ANOVA, comparing CB-5083 and CB-5083 + mirin. Statistical significance, ∗p < 0.05.
(E) Survival of RT112 cells with or without stable small hairpin RNA (shRNA) MRE11 knockdown after treatment with indicated doses of IR. RT112 cells were either treated with siRNA control or siRNA against p97. N = 3 individual biological experiments each over two technical replicates. Error bars represent ± SEM; two-way ANOVA, comparing RT112 + sip97 and RT112 shMRE11 + sip97 conditions. Statistical significance: ∗p < 0.05; ∗∗∗p < 0.001; ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001. Right: western blot of the experiment in (E).
(F) Plasma, bladder, kidney, liver, and tumor concentrations (in μM) of CB-5083 in tissue extracts from CD-1 nude mice bearing subcutaneous RT112 tumors after treatment at 25 mg/kg (N = 5). Statistical analysis: ∗p < 0.05; ∗∗p < 0.01 (unpaired t test).
(G) RT112 cells were subcutaneously injected into CD-1 nude mice to establish tumors. Tumor growth was measured after a single intraperitoneal injection of 25 mg/kg CB-5083 and radiotherapy (6 Gy, single fraction) in RT112 xenografts (N = 8 per group). ∗p < 0.05 (one-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s multiple comparisons).
(H) Small crypt assay survival for CB-5083 and mock-treated C-1 nude mice over 10 Gy (N = 3 per group), 12 Gy (N = 6 per group), and 14 Gy (N = 3 per group) of IR. Data were normalized to mean crypts per millimeter in mock-treated and CB-5083-only-treated mice.
(I) Model of the role of p97 in DSB repair pathway choice. Left: under physiological conditions, both MRE11 and the KU complex are removed from the sits of DSBs by the ATPase activity of p97 to promote HR-mediated repair. Right: inactivation of p97 causes accumulation of MRE11 and the KU complex on the sites of DSBs, leading to excessive 5′-DNA end resection, subsequent HR defects, and an increase in mutagenic SSA-mediated repair.
See also Figure S7.