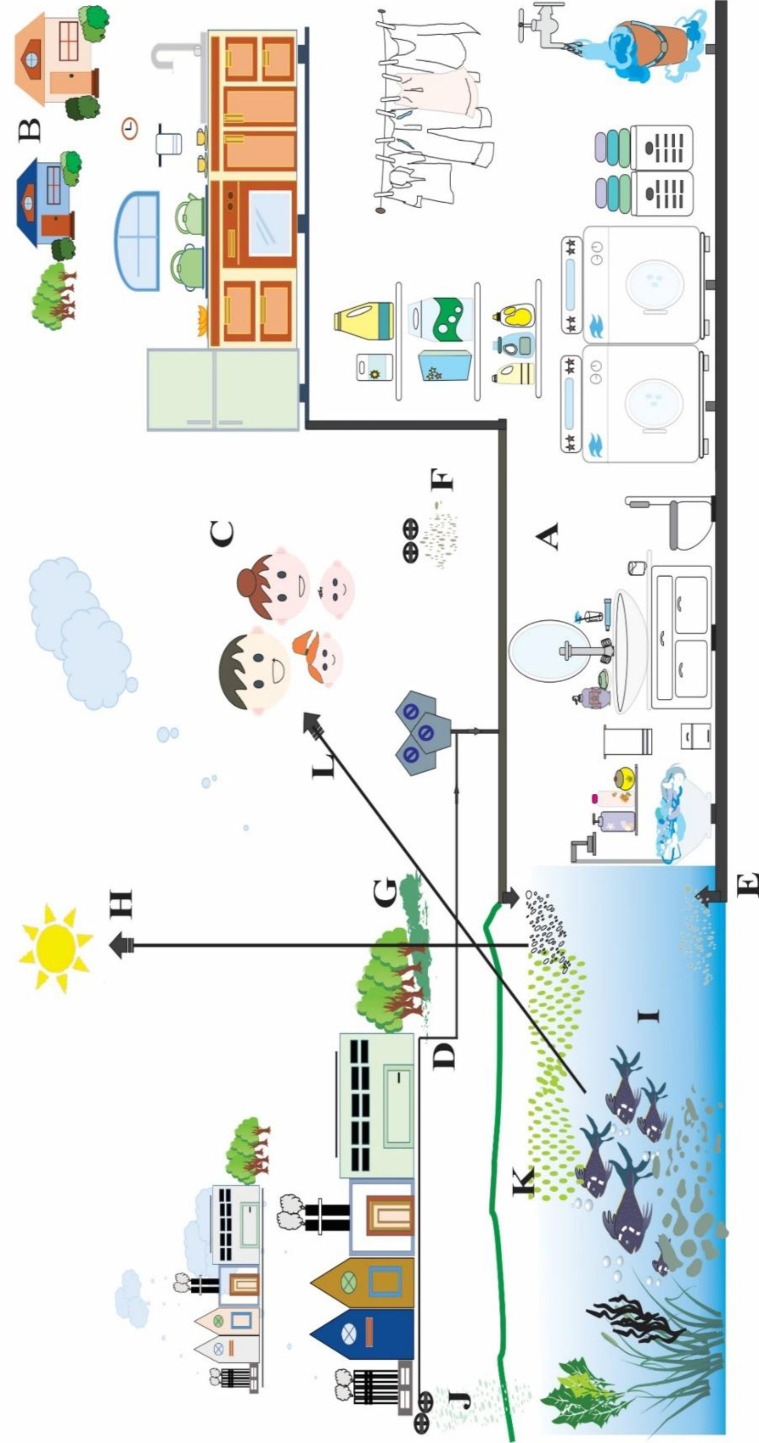
Figure 1.
Distribution of emerging contaminants of PCPs in the environment. (A) PCPs contaminants through bathing, showering, cleaning, and washing activities; (B) Overpopulated areas increase the environmental burden of PCPs contaminants; (C) Outdoor activities and odor contaminate air; (D) Industrial and manufacturer wastes enter municipal wastewater; (E) Biological active and inactive components enter the aquatic water; (F) Landfill leaks contaminate groundwater; (G) PCPs contaminant sorb onto sludge and sediment that leads to contamination of agriculture land and soil; (H) Photodegradation of PCPs; (I) Contamination of aquatic wildlife; (J) Manufacturers PCPs wastes directly contaminate air, soil and water systems; (K) Polluted aquatic system facilitate algae overgrowth; (L) Contaminated aquatic wildlife enters the food chain