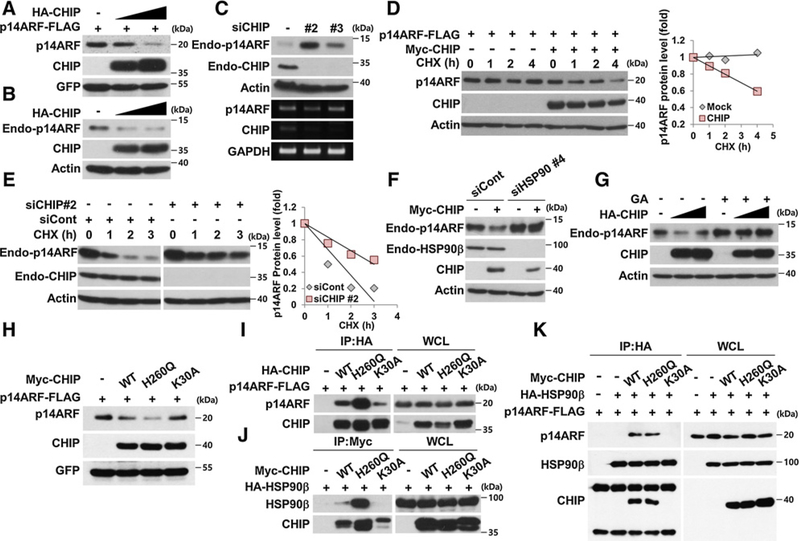
Figure 3.
HSP90 is required for CHIP-induced ubiquitylation-independent p14ARF degradation. A and B, H1299 cells were transfected with constructs as indicated. The cell lysates were immunoblotted. C, HeLa cells were transfected with 30 nmol/L CHIP siRNAs for 72 hours. mRNAs were analyzed by RT-PCR using primers specific for p14ARF and CHIP. D, H1299 cells were transfected with constructs for 24 hours, followed by cycloheximide (CHX; 100 μg/mL) treatment. The graph indicates the relative p14ARF protein levels compared with the actin protein levels. E, HeLa cells were transfected with 30 nmol/L CHIP siRNA for 72 hours and treated with cycloheximide. F, H1299 cells were transfected with 40 nmol/L HSP90β siRNA for 72 hours, and then plasmids expressing Myc-CHIP were transfected as indicated. G, HeLa cells were transfected with plasmid expressing HA-CHIP and treated with 0.5 μmol/L GA for 24 hours. H, Constructs expressing Myc-CHIP WT, H260Q, K30A, p14ARF-FLAG, and GFP were transfected into H1299 cells. I, 293T cells were transfected with plasmids as indicated. The cell lysates were immunoprecipitated using anti-HA antibody. J, 293T cells were transfected with plasmids as indicated. The cell lysates were immunoprecipitated using anti-Myc antibody. K, Plasmids were expressed in 293T cells, and the cell lysates were immunoprecipitated using anti-HA antibody as indicated. p14ARF protein expression was adjusted for comparing interactions with identical amounts of p14ARF.