Fig. 1.
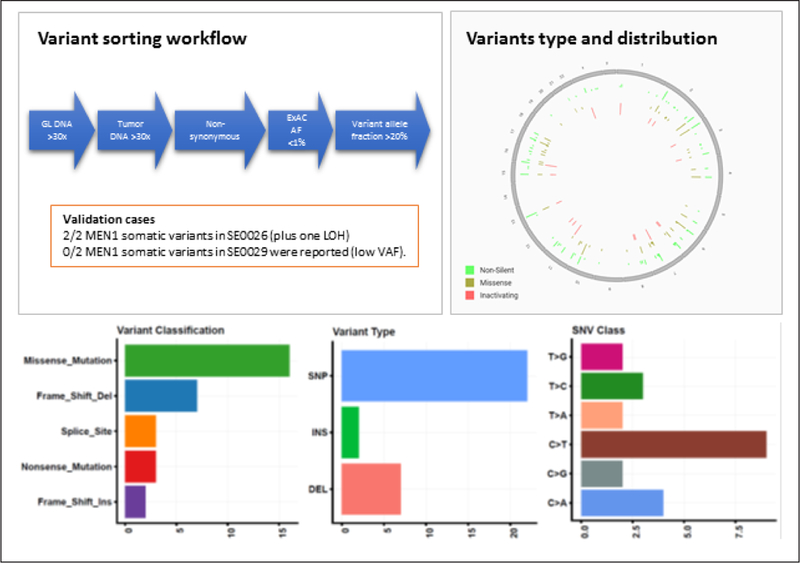
Variant sorting pipeline, variant genomic distribution, and characteristics. In order to avoid false positive calling of variants, stringent thresholds were used. We considered only variants with high coverage of both germline and tumor deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) sequencing, and with a low frequency in the general population according to the ExAC database. The cutoff stringency is demonstrated by the sorting out of the MEN1 variants in patient SE0029, due to low variant allele frequency (VAF). The homogenous variant distribution throughout the genome, the high rate of missense mutation and single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNP), and the highest rate of nucleotide transition rather than transversion, all expected in this type of analysis, support the validity of the analysis. Patients SE0026 and SE0029 have germline MEN1 pathogenic variant. DEL = deletion; GL = germline; INS = insertion; LOH = loss of heterozygosity.
