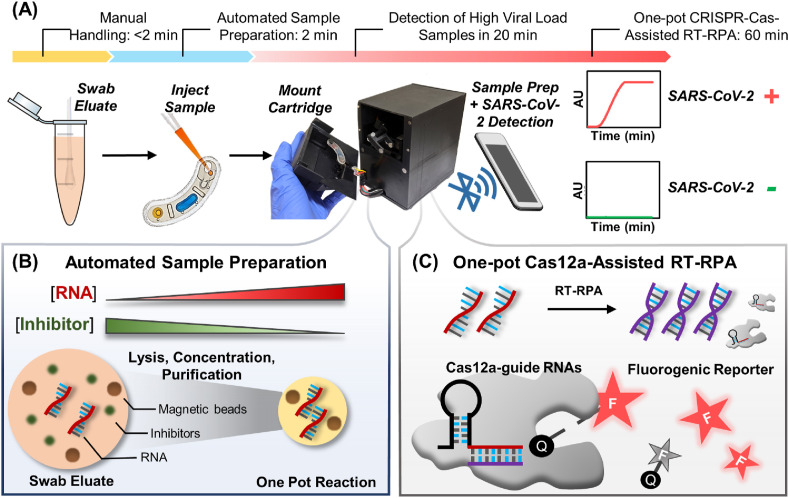
Fig. 1.
Overview of POC-CRISPR. (A) POC-CRISPR detects SARS-CoV-2 virus from unprocessed nasopharyngeal (NP) swab eluates in a sample-to-answer workflow. Upon injecting the NP swab eluate into an assay cartridge and mounting the cartridge into a palm-sized droplet magnetofluidic (DM) device, the device performs sample preparation, reaction incubation, and fluorescence-based SARS-CoV-2 detection in full automation. (B) Within the device, sample preparation is powered by DM, which leverages magnetic-based capture and transport of nucleic acid-binding magnetic beads to concentrate SARS-CoV-2 RNA and remove potential inhibitors from a large volume of NP swab eluate, as well as to transport the RNA into downstream CRISPR-Cas-assisted reaction mixture. (C) Within the reaction, SARS-CoV-2 RNA is in vitro transcribed and amplified into DNA amplicons via reverse transcription recombinase polymerase amplification (RT-RPA). The DNA amplicons then activate Cas12a-guide RNA complexes to cleave single-stranded DNA fluorogenic reporters, thereby producing fluorescent signals for detection.