Fig. 4. Aurora kinase B phosphorylates cGAS during mitosis.
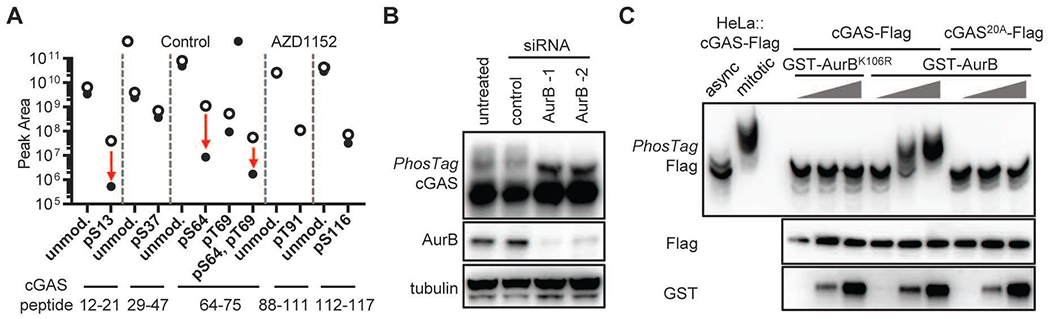
(A) BJ-5ta cells stably expressing cGAS-Flag were synchronized with Ro-3306 and released into mitosis in the absence or presence of aurora kinase B inhibitor AZD-1152 (1 μM). cGAS-Flag was isolated from the cells to quantify the level of phosphorylation by mass spectrometry. The abundance (peak area) of phosphorylation at indicated sites was quantified by PRM to identify those sensitive to AZD-1152: arrows indicate large drops from untreated (∘) to AZD-1152-treated (•) samples. (B) BJ-5ta cells were transfected with siRNA targeting Aurora kinase B (AurB) or control siRNA, or untreated for 48 hrs before synchronization with thymidine and nocodazole treatment. The level of cGAS hyperphosphorylation in mitotic cells was analyzed by PhosTag electrophoresis and immunoblotting. (C) in vitro kinase assay with recombinant cGAS-Flag and GST-AurB. cGAS phosphorylation was analyzed by PhosTag electrophoresis. The phosphorylation status of endogenous cGAS in asynchronized and mitotic HeLa cells is shown on the same blot. K106R is a mutation that inactivates Aurora kinase B.
