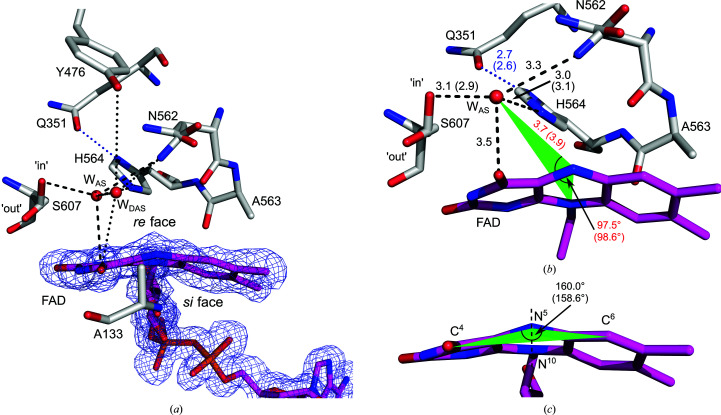
Figure 2.
The catalytic site of CtFDO:free (chain A). The cofactor, modelled in reduced form (magenta C atoms), is surrounded by the His564–Ser607 pair and additionally by Asn562, Ala563 and Tyr476 on its re face and by Ala133 on its si face. The orientation of the His564 imidazole ring is stabilized by a hydrogen bond to Gln351 (His564 Nδ1–Gln351 Oɛ1, blue dotted line). Asn562 and Ser607 have two alternative conformations. The ‘in’ (nearest standard rotamer χ1 = −65°) and ‘out’ (χ1 = 64°) conformations of Ser607 are labelled. The active-site water molecules (WAS and WDAS) binding in the catalytic site (black dashed and dotted lines, respectively) are labelled. WAS binds between His564 Nɛ2, Ser607 Oγ, Asn562 Nδ2, FAD O4 and FAD N3 in the putative binding site of the catalytically modified group of the substrate. (a) A simulated-annealing 2mF o − DF c composite OMIT map (calculated in Phenix; Terwilliger, Grosse-Kunstleve, Afonine, Moriarty, Adams et al., 2008 ▸) shown for the cofactor contoured at the 1σ level. (b) Labelled distances (differing values for chain B are given in parentheses) for WAS, which is at a distance of 3.7 Å (3.9 Å in chain B) from FAD N5 and makes an angle of 97.5° (98.6° in chain B) with the FAD N10–FAD N5 atoms, i.e. it occupies the site of oxidative attack in CtFDO. (c) The isoalloxazine bend of 20.0° (21.4° in chain B) around the FAD N5 and FAD N10 axis (dashed line). The angle between the C4, N5 and C6 atoms is labelled (the value for chain B is given in parentheses). The molecular graphics were created with PyMOL (Schrödinger).