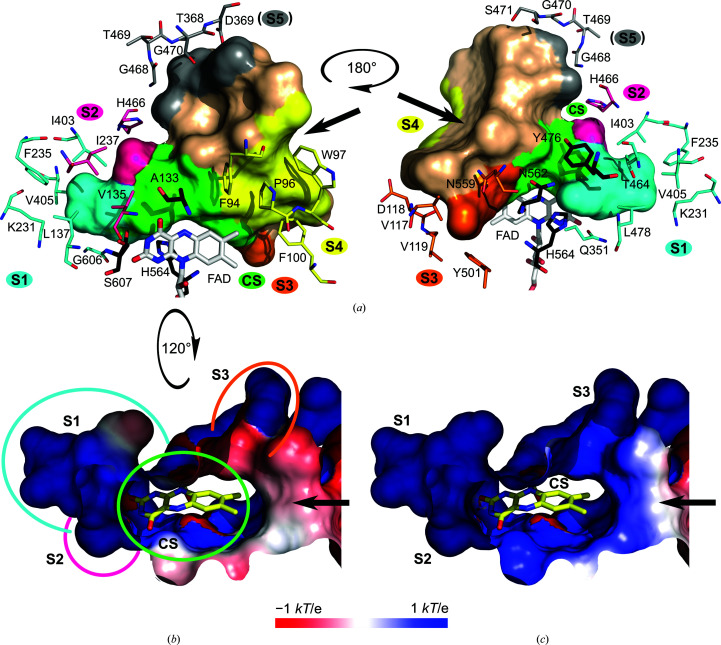
Figure 3.
The active-site pocket of CtFDO. The black arrows show the entrance to the pocket. (a) The view from two sides of the pocket in surface representation with a highlighted catalytic site (CS; green) and five subsites S1 (cyan), S2 (hot pink), S3 (orange), S4 (yellow) and the hypothetical S5 (grey). Selected surrounding residues are shown as sticks with C atoms in colours corresponding to the subsites. The residues shown with C atoms in black (Ala133, Tyr476, Asn562, His564 and Ser607) form the catalytic site. The FAD cofactor is shown with C atoms in white. The tunnel calculation was performed with HOLLOW (Ho & Gruswitz, 2008 ▸). The molecular graphics were created using PyMOL (Schrödinger). (b, c) Electrostatic potential distribution represented on the solvent-accessible surface of the active-site pocket of CtFDO at neutral pH 7 (b) and pH 5.5, corresponding to the crystallization condition (c). The catalytic site and subsites in (b) are marked by circles in colours corresponding to (a). The flavin has yellow C atoms. The electrostatic potential distribution was calculated using the Adaptive Poisson–Boltzman Solver (APBS; Baker et al., 2001 ▸) and visualized using the APBS plugin in PyMOL (Schrödinger).