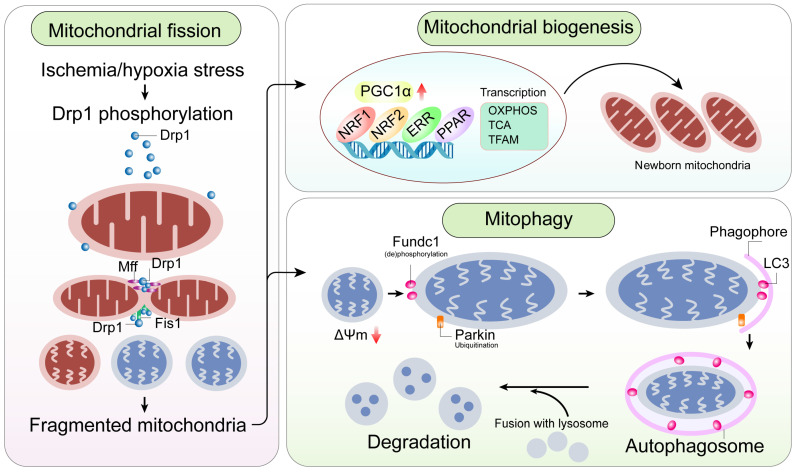
Figure 4.
A mitochondrial-centric view of coronary endothelial homeostasis. Ischemia/hypoxia promotes enhanced phosphorylation of Drp1. Subsequently, phosphorylated Drp1 (p-Drp1) oligomerizes around the mitochondrial outer membrane after being recruited and stabilized by mitochondrial receptors such as Fis1 and Mff and induces mitochondrial fission. In general, enhanced p-Drp1-mediated mitochondrial fission is accompanied by increased mitophagy and mitochondrial biogenesis. Fragmented mitochondria with low membrane potential induce PINK1 localization into the mitochondria. PINK1 recruits Parkin to the mitochondria. Concurrently, Fundc1, the mitochondria-localized mitophagy receptor, is activated through post-transcriptional phosphorylation. Mitochondria interact with LC3 on the lysosomes through Parkin and Fundc1, and form autophagosomes. Mitophagy promotes degradation of fragmented mitochondria to sustain mitochondrial homeostasis. Mitochondrial biogenesis is activated in response to mitochondrial fission or mitophagy. PGC1α is a major regulator of mitochondrial biogenesis that acts as a compensatory mechanism to mitochondrial fission or mitophagy. The other transcription factors involved in mitochondrial biogenesis are NRF1, NRF2, ERR, and PPAR. Mitochondrial biogenesis upregulates OXPHOS, TCA cycle, mtDNA and TFAM levels. Note: Drp1, dynamin-related protein 1; Fis1, mitochondrial fission factor 1; Mff, mitochondrial fission factor; NRF, nuclear respiratory factor; OXPHOS, oxidative phosphorylation; PGC1α, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor g coactivator 1α; PINK1, phosphatase and tensin homolog-induced putative kinase 1; ROS, reactive oxygen species; TCA, tricarboxylic acid; TFAM, mitochondrial transcription factor A.