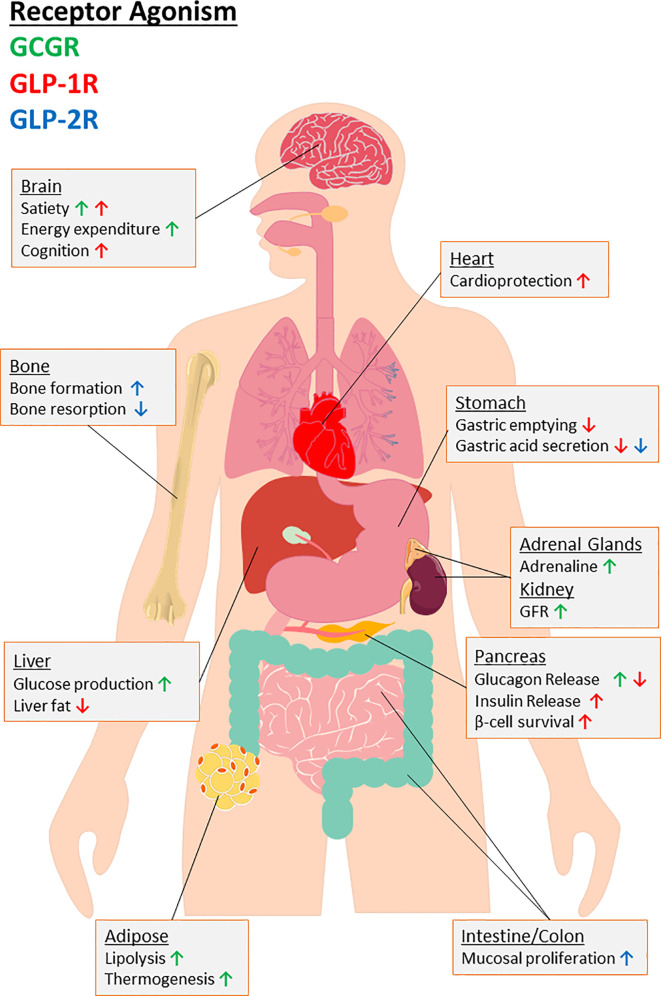
Figure 3.
An overview of the biological consequences for agonism of target receptors of major PGDP’s, namely glucagon receptor (GCGR) and glucagon-like peptide-1 and -2 receptors (GLP-1R, GLP-2R). Organ-specific actions are provided with arrows indicating up or downregulation of specific effects to highlight the therapeutic potential for multiagonism in relation to PGDP’s. As indicated by the key, the colour of arrow indicates the receptor interactions responsible. “GFR” indicates glomerular filtration rate.