Figure 2.
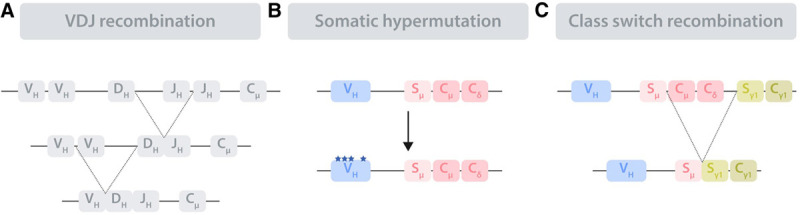
Schematic representation of the immunoglobulin remodeling processes. The immunoglobulin loci undergo diverse remodeling processes in order to encode a functional, high-affinity BCR. (A), Immunoglobulin remodeling starts in bone marrow precursor B cells by V(D)J recombination, a process that assembles 3 (V, D, and J) or 2 (V and J) genes in the immunoglobulin loci encoding for the immunoglobulin heavy locus (IGH) and light chain (not shown), respectively. (B), Somatic hypermutation takes place in the GC DZ compartment and introduces point mutations, deletions, and duplications in the rearranged V regions of the immunoglobulin loci. (C), Class switch recombination targets the constant (C) region of the IGH, leading to the replacement of the original Cμ and Cδ with one of several other C regions (in the scheme Cγ1), each resulting in an antibody with different effector functions. The exchange occurs at the switch (S) regions. BCR = B-cell receptor; D = diversity; DZ = dark zone; GC = germinal center; J = joining; V = variable.
