Fig. 2.
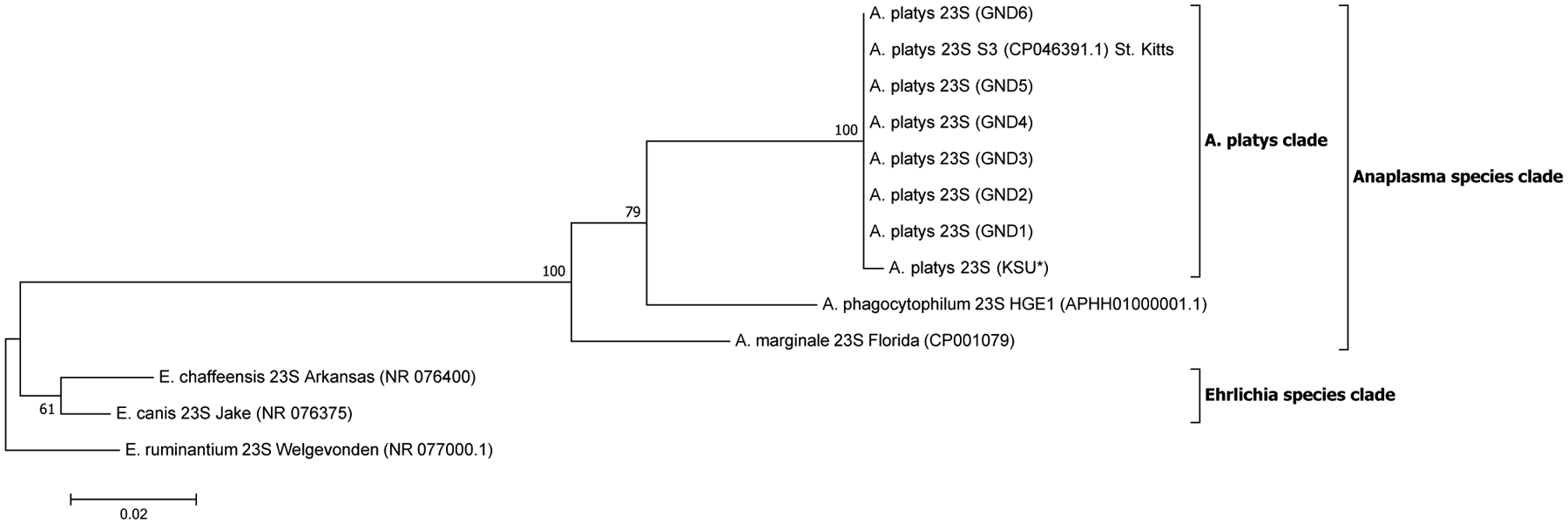
Maximum likelihood (ML) phylogenetic analysis of A. platys 23S rRNA gene sequences. Phylogenetic relationships between A. platys and homologous 23S sequences from A. marginale, A. phagocytophilum, E. canis, E. chaffeensis and E. ruminantium were established. Bootstrap values are shown by numbers at each internal node and represent the percentage of 1000 replicates for which the same branching pattern was obtained. There were a total of 2794 positions in the dataset. Both NJ and UPGMA analyses for 23S sequences generated trees with similar topology with those derived from ML analysis (Supplementary Fig. 2a and b). A total of 13 nucleotide sequences were used in the final analysis and the scale-bar represents a 2% nucleotide sequence divergence. Pairwise identity results of these data are given in Supplementary Table 2 and Data 2. (KSU*) = sample obtained from a dog tested positive in Florida, USA. GND = Grenada samples.
