Figure 3.
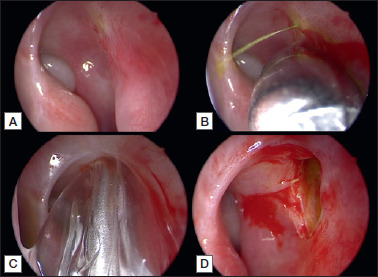
Using 30° endoscope, the stenotic neo-rhinostomy is identified thanks to soft lavage of the lacrimal pathway with fluorescein, performed by an ophthalmologist (A); identification of the exact position of the neo-rhinostomy thanks to “high” pressure lavage of the lacrimal pathway with fluorescein (B); pneumatic dilatation of the neo-rhinostomy using a trans-nasal balloon catheter (C); enlarged revised neo-rhinostomy (D).
