Fig. 2.
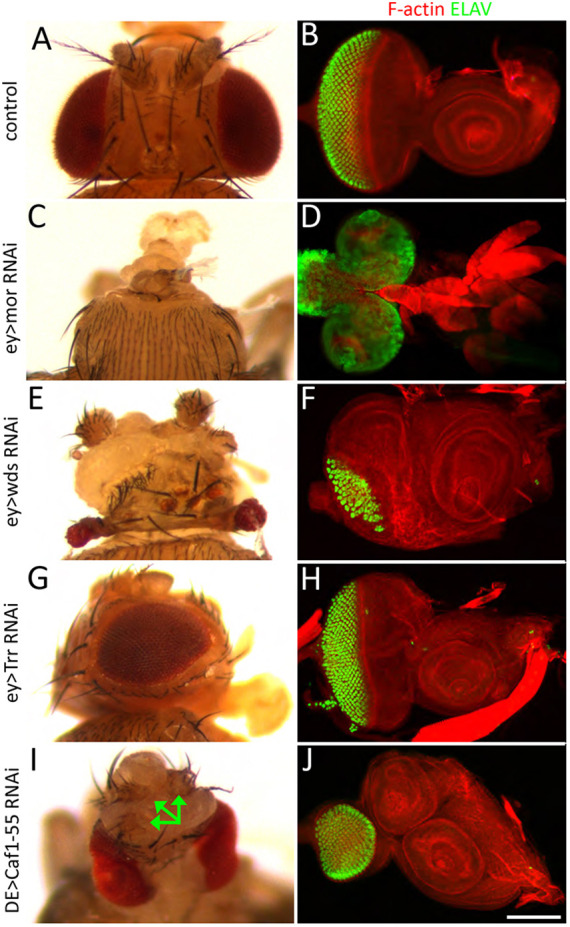
The development of the eye-antennal disc is regulated by chromatin-modifying proteins. (A,C,E,G,I) Adult heads. (B,D,F,H,J) Third instar eye-antennal discs stained for F-actin (red) and ELAV (green). (A,B) A pair of wild-type eye-antennal discs give rise to the external surface of the adult head. (C-J) Knockdown of chromatin-modifying proteins result in a variety of defects, including complete loss of the head (C,D), severe head defects (E,F), small rough eyes (G,H) and antennal duplications (I,J). The arrows in I point to three of the four antennae that are formed when Caf1-55 is knocked down. Scale bar: 50 µm.
