Fig. 3. The 47D11 epitope comprises a mutationally constrained hydrophobic pocket that is normally shielded by glycan N343.
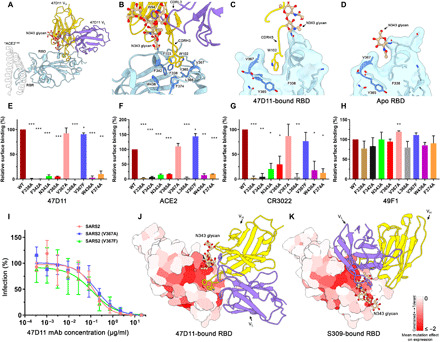
(A) Ribbon diagram of the SARS2-S RBD in complex with the 47D11 antibody Fab fragment. For comparison, residues 1 to 84 of the RBD-bound ACE2 (PDB ID: 6M0J) are shown as a silhouette. (B) Close-up view of the 47D11 epitope with the hydrophobic pocket residues shown as sticks and colored dark blue. The N343 glycan is shown in ball-and-stick representation and colored tan. For clarity, only the core pentasaccharide is shown. (C) Slice through the surface rendered 47D11-bound SARS2-S RBD. The helix encompassing residues 365 to 370 is shown in darker blue. (D) Equivalent view as shown in (C) for the apo RBD (PDB ID: 6VYB). (E) Relative binding of 47D11, (F) ACE2, and (G) CR3022 to cell surface–expressed SARS2-S, determined by fluorescence-activated cell sorting. (H) Relative binding of an anti-FLAG antibody to permeabilized cells expressing the full-length SARS2 spike epitope mutants, determined by fluorescence-activated cell sorting. The data were analyzed by the unpaired, two-tailed Student’s t test using GraphPad Prism 7.0. P < 0.05 was considered significant (*P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, and ***P < 0.0001). (I) Antibody-mediated neutralization of infection of luciferase-encoding VSV particles pseudotyped with wild-type, V367A, or V367F SARS2-S. (J) Surface representation of the 47D11-bound SARS2-S RBD colored according to mean mutation effect on expression (red indicates more constrained) (58). The Fab is shown as a ribbon diagram. (K) As shown in (E) for the S309-bound SARS2 RBD.
