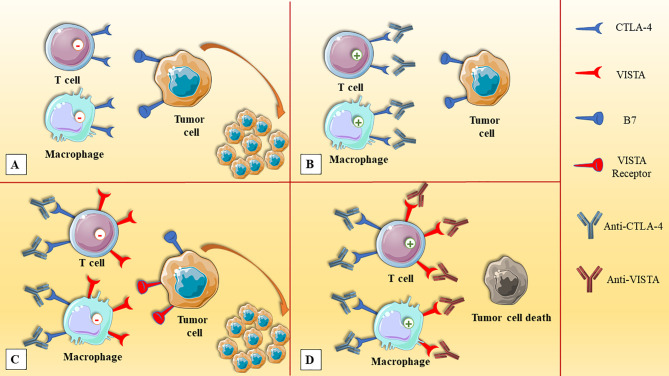
Figure 2.
The upregulation of VISTA in prostate cancer after anti-CTLA-4 therapy. (A) The expression of CTLA-4 on immune cells, e.g., T cells and macrophages, and its interaction with tumoral cells can attenuate anti-tumoral immune responses. (B) The administration of anti-CTLA-4 can stimulate anti-tumoral immune responses. (C) After anti-CTLA-4 therapy, the upregulation of VISTA inhibits immune cell activation and leads to tumor expansion. (D) Dual VISTA/CTLA-4 blockade can elicit synergistic responses and leads to the elimination of prostate cancer cells. CTLA-4, cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-associated protein-4; VISTA, V-domain Ig suppressor of T cell activation.