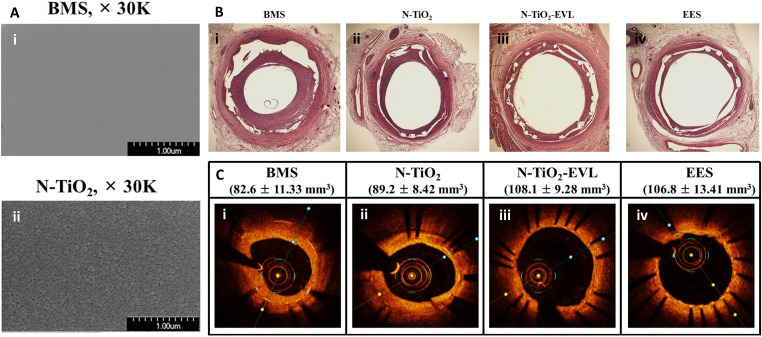
FIG. 4.
(a) SEM images of (i) BMS and (ii) N–TiO2 film deposited on a bare stent. (b) Histopathological H&E staining and (c) optical coherence tomography of porcine coronary arteries implanted with (i) BMS, (ii) N–TiO2, (iii) N–TiO2 with everolimus, and (iv) EES for 4 weeks. The restenosis area was significantly decreased in the N–TiO2-everolimus group compared to that in the BMS group and was at par with the commercial EES. Reprinted with permission from Park et al., Mater. Sci. Eng.: C 91, 615–623 (2018). Copyright 2018 Elsevier. (BMS: bare-metal stent; N–TiO2: nitrogen-doped TiO2 film; EES: everolimus-eluting stent.)