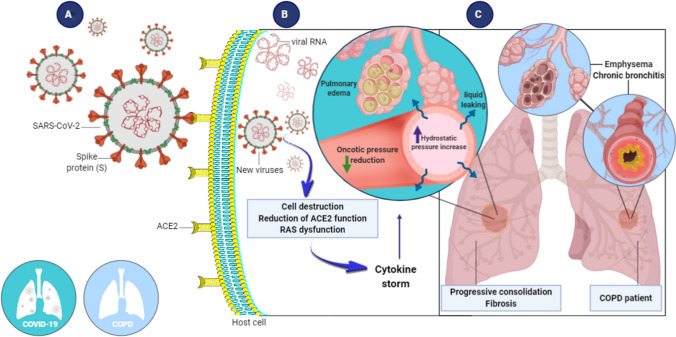
Fig. 1.
Human pulmonary cell infection by SARS-CoV-2 and morphological and functional outcomes. A SARS-CoV-2 is transmitted through respiratory droplets, replicates in the respiratory tract, and infects pulmonary cells by attaching S-proteins to ACE2 membrane receptors on host cells. B Once inside host cells, new viruses are formed, resulting in a cytokine storm. Hydrostatic pressure increases in capillary walls, causing an increase in capillary permeability. C As a result, fluid leaks from the capillary into the interstitial and alveolar space, resulting in edema. In some cases, fibrosis develops. The left lung represents COVID-19. The right lung represents COPD. ACE2, angiotensin-I-converting enzyme 2; RAS, renin-angiotensin system; COPD, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease