Fig. 3. Activation of the Gi-cascade in ACC L5-PCs reduces premature responding in a pharmacological challenge of impulsivity.
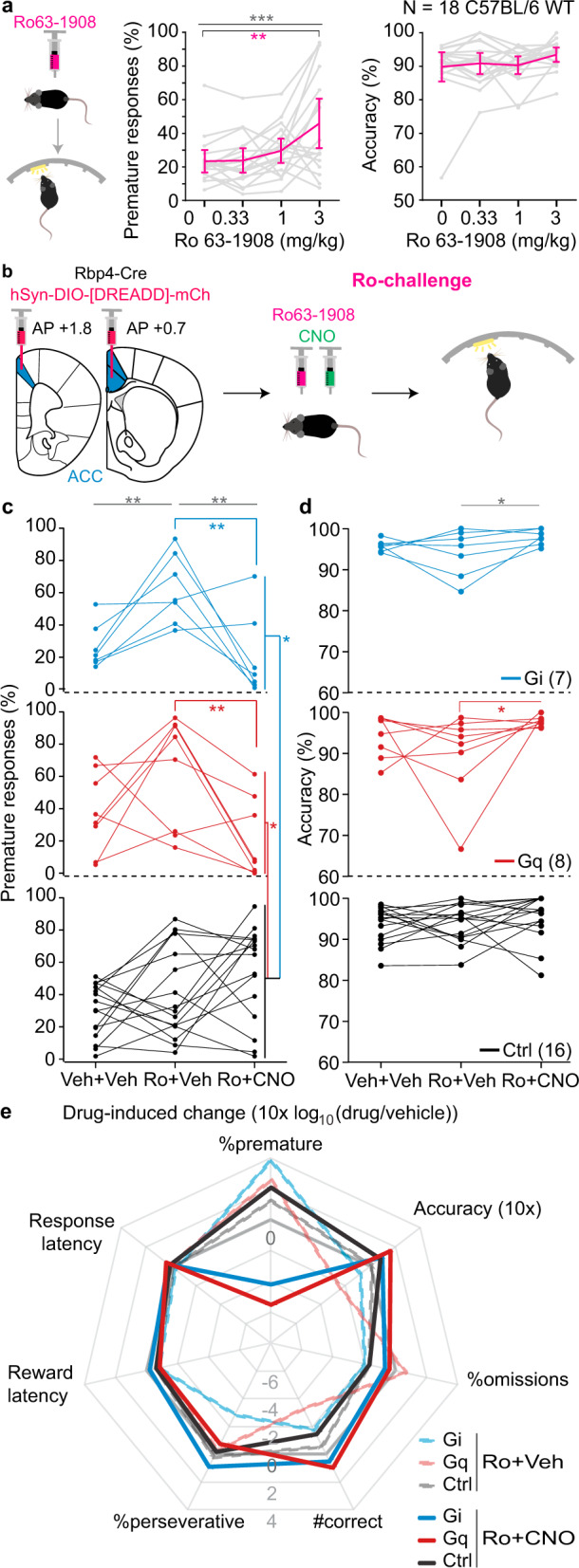
a Premature responding and accuracy after injection of vehicle (0) or indicated doses of Ro 63-1903 (Ro) in a separate cohort of 18 wildtype mice. Error bars, C.I. b Experimental schedule applying Ro as impulsivity challenge and CNO before testing in the 5-CSRTT in a subset of the DREADD-transduced Rbp4-Cre cohort evaluated in Fig. 2. %premature responses (c) and attentional accuracy (d) observed after application of 3 mg/kg Ro 63-1908 (Ro) and additional application of CNO (Ro+CNO). 1 mg/kg CNO was used for the Gq-group and a subset of Ctrl mice, 10 mg/kg CNO was used for the remainder. In a, c, d, grey asterisks indicate significant main effect of drug condition across all groups (RM-ANOVA), coloured asterisks below horizontal lines indicate significant paired post-hoc comparisons between the indicated drug condition (vehicle and 3 mg/kg Ro in a, Ro+Veh and Ro+CNO in c, d) in the groups indicated by the colour (Sidak); coloured asterisks on the right indicate significant pairwise post-hoc comparisons between the group indicated by the colour (Gi, blue; Gq, red; Ctrl, black) at the Ro+CNO condition (Sidak). e Response profiles of Ro- (dashed lines of reduced opacity) or Ro+CNO-induced (solid lines) changes relative to the vehicle/vehicle condition measured as log10-transform of the within-subject ratio (value after drug/value after vehicle) for relevant behavioural performance parameters on the 5-CSRTT are shown for the three groups as indicated in the legend; grey solid line indicates 0-lattitude (no CNO-induced change). N-numbers for c–e stated in d. See Supplementary Tables 3 and 7–10 for reasons for varying N-numbers across experiments, further statistical analysis, and absolute response numbers, respectively. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P ≤ 0.001; individual dot-lines represent subjects.
