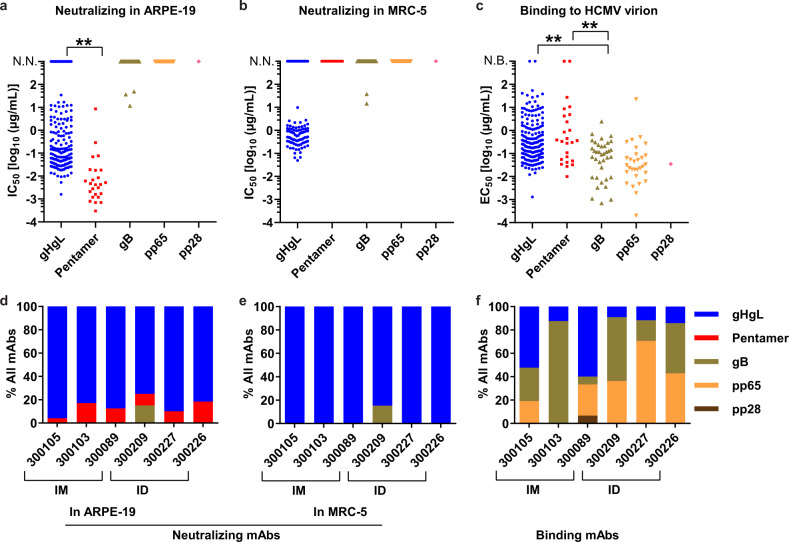
Fig. 2. V160 induces neutralizing and binding antibodies targeting diverse antigens in the HCMV-seronegative subjects.
Neutralization potency was quantified by IC50, defined as the concentration of the IgG required to block 50% viral entry into ARPE-19/MRC-5 cells. The binding affinity of the antibodies to HCMV virion was quantified by EC50, defined as the concentration of the IgG required to achieve 50% of the maximal binding signals in ELISA. a The neutralization potency in ARPE-19 cells of mAbs grouped based on their antigen specificity. b The neutralization potency in MRC-5 cells of mAbs grouped based on their antigen specificity. c The relative binding affinity of mAbs based on their antigen specificity. d Distribution of neutralizing mAbs targeting different antigens in each of the six subjects as assessed in ARPE-19 cells and e MRC-5 cells. f Distribution of binding mAbs targeting different antigens in each of the six subjects. The subjects are indicated with the subject numbers 300105, 300103, 300089 in the intramuscular injection group (IM), and 300209, 300227, 300226 in the intradermal injection group (ID). Unpaired two-tailed t test was performed. Differences with statistical significance are shown with p values, “**” indicates p < 0.001. The data are representative of two independent experiments. N.N. indicates no neutralizing activity. N.B. indicates no binding to the HCMV virion.